概要
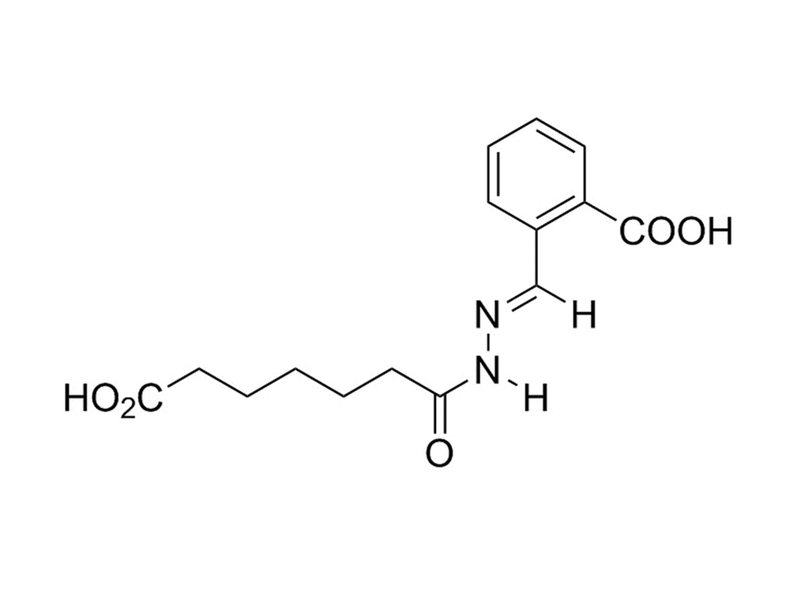
Inducer of definitive endoderm 1 (IDE1) induces differentiation of mouse or human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) by activating SMAD2 phosphorylation and NODAL expression (Borowiak et al.). At EC₅₀ = 125 nM, SOX17 expression was induced in mouse ES cells.
DIFFERENTIATION
· Induces differentiation of mouse or human ES cells to definitive endoderm in the absence of Activin A, NODAL, or feeder cells (Borowiak et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
· Induces differentiation of mouse or human ES cells to definitive endoderm in the absence of Activin A, NODAL, or feeder cells (Borowiak et al.).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | IDE1 | 72512, 72514 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | IDE1 | 72512, 72514 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (1)
Cell stem cell 2009 APR
Small molecules efficiently direct endodermal differentiation of mouse and human embryonic stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
An essential step for therapeutic and research applications of stem cells is the ability to differentiate them into specific cell types. Endodermal cell derivatives, including lung, liver, and pancreas, are of interest for regenerative medicine, but efforts to produce these cells have been met with only modest success. In a screen of 4000 compounds, two cell-permeable small molecules were indentified that direct differentiation of ESCs into the endodermal lineage. These compounds induce nearly 80% of ESCs to form definitive endoderm, a higher efficiency than that achieved by Activin A or Nodal, commonly used protein inducers of endoderm. The chemically induced endoderm expresses multiple endodermal markers, can participate in normal development when injected into developing embryos, and can form pancreatic progenitors. The application of small molecules to differentiate mouse and human ESCs into endoderm represents a step toward achieving a reproducible and efficient production of desired ESC derivatives.

 网站首页
网站首页