概要
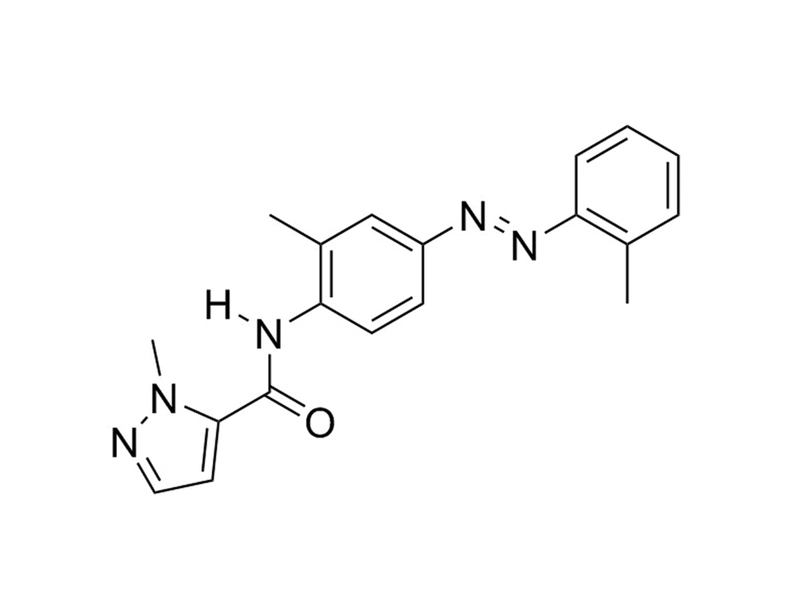
CH223191 is a potent and specific antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) that blocks activation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD; IC₅₀ = 0.03 µM; Kim et al.). It prevents the induction of cytochrome P450 1A1 by TCDD in HepG2 cells and in livers of mice (Kim et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Induces expansion of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in culture (Boitano et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Induces expansion of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in culture (Boitano et al.).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
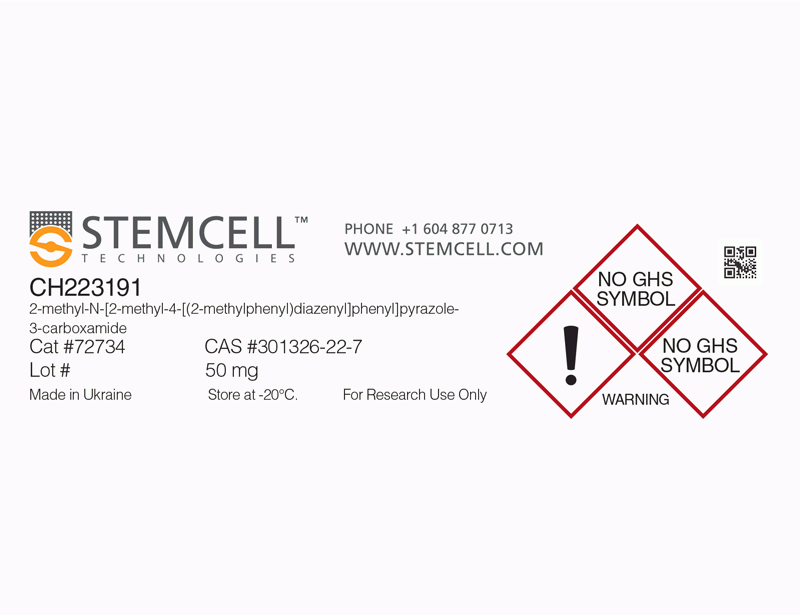
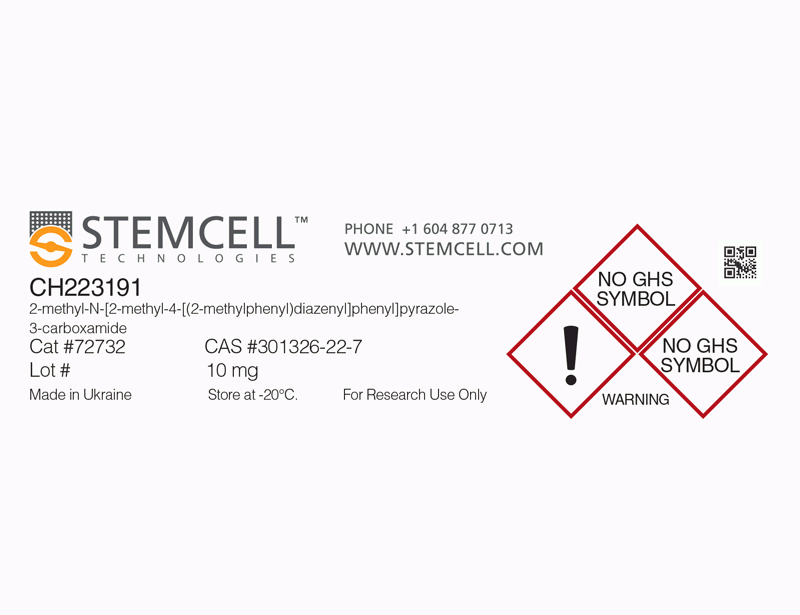
| Product Information Sheet | CH223191 | 72732, 72734 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | CH223191 | 72732, 72734 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (2)
Science (New York, N.Y.) 2010 SEP
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonists promote the expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Although practiced clinically for more than 40 years, the use of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplants remains limited by the ability to expand these cells ex vivo. An unbiased screen with primary human HSCs identified a purine derivative, StemRegenin 1 (SR1), that promotes the ex vivo expansion of CD34+ cells. Culture of HSCs with SR1 led to a 50-fold increase in cells expressing CD34 and a 17-fold increase in cells that retain the ability to engraft immunodeficient mice. Mechanistic studies show that SR1 acts by antagonizing the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). The identification of SR1 and AHR modulation as a means to induce ex vivo HSC expansion should facilitate the clinical use of HSC therapy.
Molecular pharmacology 2006 JUN
Novel compound 2-methyl-2H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (2-methyl-4-o-tolylazo-phenyl)-amide (CH-223191) prevents 2,3,7,8-TCDD-induced toxicity by antagonizing the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Abstract
Abstract
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a widespread environmental pollutant with many toxic effects, including endocrine disruption, reproductive dysfunction, immunotoxicity, liver damage, and cancer. These are mediated by TCDD binding to and activating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. In this regard, targeting the AhR using novel small molecule inhibitors is an attractive strategy for the development of potential preventive agents. In this study, by screening a chemical library composed of approximately 10,000 compounds, we identified a novel compound, 2-methyl-2H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (2-methyl-4-o-tolylazo-phenyl)-amide (CH-223191), that potently inhibits TCDD-induced AhR-dependent transcription. In addition, CH-223191 blocked the binding of TCDD to AhR and inhibited TCDD-mediated nuclear translocation and DNA binding of AhR. These inhibitory effects of CH-223191 prevented the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes, target genes of the AhR. Unlike many known antagonists of AhR, CH-223191 did not have detectable AhR agonist-like activity or estrogenic potency, suggesting that CH-223191 is a specific antagonist of AhR. It is noteworthy that CH-223191 potently prevented TCDD-elicited cytochrome P450 induction, liver toxicity, and wasting syndrome in mice. Taken together, these results demonstrate that this novel compound, CH-223191, may be a useful agent for the study of AhR-mediated signal transduction and the prevention of TCDD-associated pathology.

 网站首页
网站首页