概要
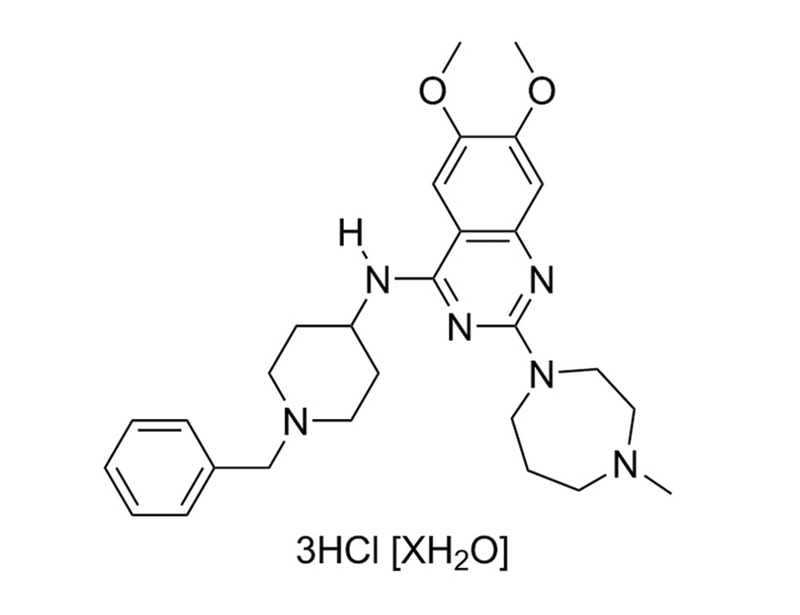
BIX01294 is a very specific inhibitor of the G9a (IC₅₀ = 1.9 µM) and G9a-like (GLP, IC₅₀ = 0.7 µM) histone methyltransferases. These methyltransferases target the lysine 9 position on histone 3 (H3K9). BIX01294 inhibits G9a and GLP by occupying the histone binding site, preventing interaction with histones (Chang et al., Kubicek et al.). This product is supplied as the trihydrochloride hydrate form of the molecule.
REPROGRAMMING
· Enhances reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblasts or fetal neural progenitor cells to induced pluripotent stem cells without using c-Myc and SOX2 (Shi et al. 2008a, Shi et al. 2008b).
REPROGRAMMING
· Enhances reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblasts or fetal neural progenitor cells to induced pluripotent stem cells without using c-Myc and SOX2 (Shi et al. 2008a, Shi et al. 2008b).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet 1 | BIX01294 (Trihydrochloride Hydrate) | 72042, 72044 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet 2 | BIX01294 (Trihydrochloride Hydrate) | 72042, 72044 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | BIX01294 (Trihydrochloride Hydrate) | 72042, 72044 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (4)
Nature structural & molecular biology 2009 MAR
Structural basis for G9a-like protein lysine methyltransferase inhibition by BIX-01294.
Abstract
Abstract
Histone lysine methylation is an important epigenetic mark that regulates gene expression and chromatin organization. G9a and G9a-like protein (GLP) are euchromatin-associated methyltransferases that repress transcription by methylating histone H3 Lys9. BIX-01294 was originally identified as a G9a inhibitor during a chemical library screen of small molecules and has previously been used in the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Here we present the crystal structure of the catalytic SET domain of GLP in complex with BIX-01294 and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine. The inhibitor is bound in the substrate peptide groove at the location where the histone H3 residues N-terminal to the target lysine lie in the previously solved structure of the complex with histone peptide. The inhibitor resembles the bound conformation of histone H3 Lys4 to Arg8, and is positioned in place by residues specific for G9a and GLP through specific interactions.
Cell stem cell 2008 NOV
Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic fibroblasts by Oct4 and Klf4 with small-molecule compounds.
Abstract
Abstract
Somatic cells can be induced into pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) with a combination of four transcription factors, Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/c-Myc or Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/LIN28. This provides an enabling platform to obtain patient-specific cells for various therapeutic and research applications. However, several problems remain for this approach to be therapeutically relevant due to drawbacks associated with efficiency and viral genome integration. Recently, it was shown that neural progenitor cells (NPCs) transduced with Oct4/Klf4 can be reprogrammed into iPSCs. However, NPCs express Sox2 endogenously, possibly facilitating reprogramming in the absence of exogenous Sox2. In this study, we identified a small-molecule combination, BIX-01294 and BayK8644, that enables reprogramming of Oct4/Klf4-transduced mouse embryonic fibroblasts, which do not endogenously express the factors essential for reprogramming. This study demonstrates that small molecules identified through a phenotypic screen can compensate for viral transduction of critical factors, such as Sox2, and improve reprogramming efficiency.
Cell stem cell 2008 JUN
A combined chemical and genetic approach for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Molecular cell 2007 FEB
Reversal of H3K9me2 by a small-molecule inhibitor for the G9a histone methyltransferase.
Abstract
Abstract
Histone lysine methylation has important roles in the organization of chromatin domains and the regulation of gene expression. To analyze its function and modulate its activity, we screened for specific inhibitors against histone lysine methyltransferases (HMTases) using recombinant G9a as the target enzyme. From a chemical library comprising 125,000 preselected compounds, seven hits were identified. Of those, one inhibitor, BIX-01294 (diazepin-quinazolin-amine derivative), does not compete with the cofactor S-adenosyl-methionine, and selectively impairs the G9a HMTase and the generation of H3K9me2 in vitro. In cellular assays, transient incubation of several cell lines with BIX-01294 lowers bulk H3K9me2 levels that are restored upon removal of the inhibitor. Importantly, chromatin immunoprecipitation at several G9a target genes demonstrates reversible reduction of promoter-proximal H3K9me2 in inhibitor-treated mouse ES cells and fibroblasts. Our data identify a biologically active HMTase inhibitor that allows for the transient modulation of H3K9me2 marks in mammalian chromatin.

 网站首页
网站首页