概要
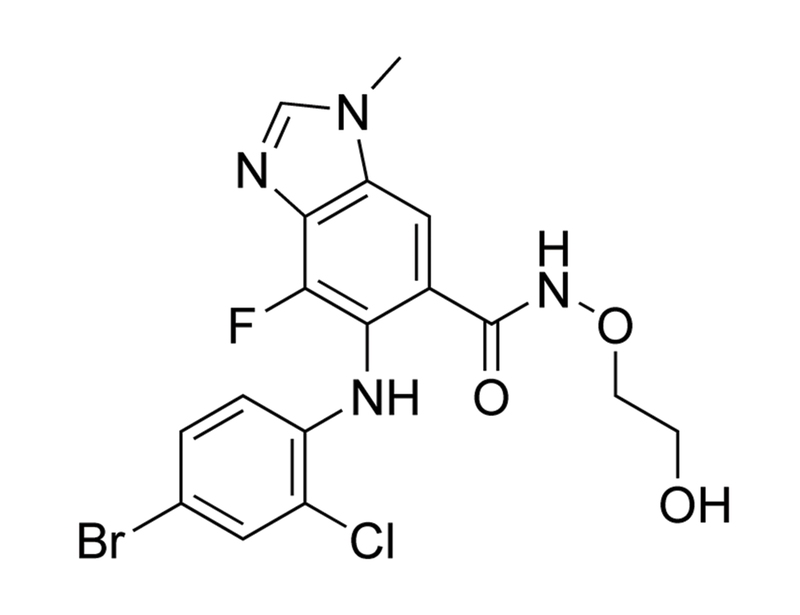
AZD6244 is a potent, highly selective inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinases MEK1 (IC₅₀ = 14 nM) and MEK2 (Kd = 530 nM; Yeh et al.; Davis et al.). It is a tight-binding noncompetitive inhibitor that does not bind in the ATP binding pocket of MEK (Huynh et al.). It also shows micromolar binding to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; Davis et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits growth of several tumor cell lines but not normal fibroblast lines, and inhibits tumor growth in a colorectal xenograft tumor model (Yeh et al.).
· Inhibits proliferation and induces differentiation and apoptosis in multiple tumor cell lines and tumor xenograft models, especially those containing BRAF or RAS mutations (Davies et al.).
· Inhibits proliferation of breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, especially those containing RAF and RAS mutations, respectively (Garon et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits growth of several tumor cell lines but not normal fibroblast lines, and inhibits tumor growth in a colorectal xenograft tumor model (Yeh et al.).
· Inhibits proliferation and induces differentiation and apoptosis in multiple tumor cell lines and tumor xenograft models, especially those containing BRAF or RAS mutations (Davies et al.).
· Inhibits proliferation of breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, especially those containing RAF and RAS mutations, respectively (Garon et al.).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet 1 | AZD6244 | 72992, 72994 | BX23470, BX29462, SC08602, SC05627 | English |
| Product Information Sheet 2 | AZD6244 | 72992, 72994 | All other lots | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | AZD6244 | 72992, 72994 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (6)
JAMA 2014
Effect of selumetinib vs chemotherapy on progression-free survival in uveal melanoma: a randomized clinical trial.
Abstract
Abstract
IMPORTANCE: Uveal melanoma is characterized by mutations in GNAQ and GNA11, resulting in mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation. OBJECTIVE: To assess the efficacy of selumetinib, a selective, non-adenosine triphosphate competitive inhibitor of MEK1 and MEK2, in uveal melanoma. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS: Randomized, open-label, phase 2 clinical trial comparing selumetinib vs chemotherapy conducted from August 2010 through December 2013 among 120 patients with metastatic uveal melanoma at 15 academic oncology centers in the United States and Canada. INTERVENTIONS: One hundred one patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive selumetinib, 75 mg orally twice daily on a continual basis (n = 50), or chemotherapy (temozolomide, 150 mg/m2 orally daily for 5 of every 28 days, or dacarbazine, 1000 mg/m2 intravenously every 21 days [investigator choice]; n = 51) until disease progression, death, intolerable adverse effects, or withdrawal of consent. After primary outcome analysis, 19 patients were registered and 18 treated with selumetinib without randomization to complete the planned 120-patient enrollment. Patients in the chemotherapy group could receive selumetinib at the time of radiographic progression. MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES: Progression-free survival, the primary end point, was assessed as of April 22, 2013. Additional end points, including overall survival, response rate, and safety/toxicity, were assessed as of December 31, 2013. RESULTS: Median progression-free survival among patients randomized to chemotherapy was 7 weeks (95% CI, 4.3-8.4 weeks; median treatment duration, 8 weeks; interquartile range [IQR], 4.3-16 weeks) and among those randomized to selumetinib was 15.9 weeks (95% CI, 8.4-21.1 weeks; median treatment duration, 16.1 weeks; IQR, 8.1-25.3 weeks) (hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.30-0.71; P textless .001). Median overall survival time was 9.1 months (95% CI, 6.1-11.1 months) with chemotherapy and 11.8 months (95% CI, 9.8-15.7 months) with selumetinib (hazard ratio, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.41-1.06; P = .09). No objective responses were observed with chemotherapy. Forty-nine percent of patients treated with selumetinib achieved tumor regression, with 14% achieving an objective radiographic response to therapy. Treatment-related adverse events were observed in 97% of patients treated with selumetinib, with 37% requiring at least 1 dose reduction. CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE: In this hypothesis-generating study of patients with advanced uveal melanoma, selumetinib compared with chemotherapy resulted in a modestly improved progression-free survival and response rate; however, no improvement in overall survival was observed. Improvement in clinical outcomes was accompanied by a high rate of adverse events. TRIAL REGISTRATION: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01143402.
Nature biotechnology 2011
Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity.
Abstract
Abstract
We tested the interaction of 72 kinase inhibitors with 442 kinases covering textgreater80% of the human catalytic protein kinome. Our data show that, as a class, type II inhibitors are more selective than type I inhibitors, but that there are important exceptions to this trend. The data further illustrate that selective inhibitors have been developed against the majority of kinases targeted by the compounds tested. Analysis of the interaction patterns reveals a class of 'group-selective' inhibitors broadly active against a single subfamily of kinases, but selective outside that subfamily. The data set suggests compounds to use as tools to study kinases for which no dedicated inhibitors exist. It also provides a foundation for further exploring kinase inhibitor biology and toxicity, as well as for studying the structural basis of the observed interaction patterns. Our findings will help to realize the direct enabling potential of genomics for drug development and basic research about cellular signaling.
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2010
Identification of common predictive markers of in vitro response to the Mek inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) in human breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
Abstract
Abstract
Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) is a tight-binding, uncompetitive inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MEK) 1 and 2 currently in clinical development. We evaluated the effects of selumetinib in 31 human breast cancer cell lines and 43 human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines to identify characteristics correlating with in vitro sensitivity to MEK inhibition. IC(50) textless1 micromol/L (considered sensitive) was seen in 5 of 31 breast cancer cell lines and 15 of 43 NSCLC cell lines, with a correlation between sensitivity and raf mutations in breast cancer cell lines (P = 0.022) and ras mutations in NSCLC cell lines (P = 0.045). Evaluation of 27 of the NSCLC cell lines with Western blots showed no clear association between MEK and phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway activation and sensitivity to MEK inhibition. Baseline gene expression profiles were generated for each cell line using Agilent gene expression arrays to identify additional predictive markers. Genes associated with differential sensitivity to selumetinib were seen in both histologies, including a small number of genes in which differential expression was common to both histologies. In total, these results suggest that clinical trials of selumetinib in breast cancer and NSCLC might select patients whose tumors harbor raf and ras mutations, respectively.
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2007
AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical
Abstract
Abstract
Constitutive activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in human cancers is often associated with mutational activation of BRAF or RAS. MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2 kinases lie downstream of RAS and BRAF and are the only acknowledged activators of ERK1/2, making them attractive targets for therapeutic intervention. AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) is a potent, selective, and ATP-uncompetitive inhibitor of MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2. In vitro cell viability inhibition screening of a tumor cell line panel found that lines harboring BRAF or RAS mutations were more likely to be sensitive to AZD6244. The in vivo mechanisms by which AZD6244 inhibits tumor growth were investigated. Chronic dosing with 25 mg/kg AZD6244 bd resulted in suppression of growth of Colo-205, Calu-6, and SW-620 xenografts, whereas an acute dose resulted in significant inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Increased cleaved caspase-3, a marker of apoptosis, was detected in Colo-205 and Calu-6 but not in SW-620 tumors where a significant decrease in cell proliferation was detected. Chronic dosing of AZD6244 induced a morphologic change in SW-620 tumors to a more differentiated phenotype. The potential of AZD6244 in combination with cytotoxic drugs was evaluated in mice bearing SW-620 xenografts. Treatment with tolerated doses of AZD6244 and either irinotecan or docetaxel resulted in significantly enhanced antitumor efficacy relative to that of either agent alone. These results indicate that AZD6244 has potential to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis and differentiation, but the response varies between different xenografts. Moreover, enhanced antitumor efficacy can be obtained by combining AZD6244 with the cytotoxic drugs irinotecan or docetaxel.
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2007
Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Abstract
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy in Asia and Africa. We previously reported that overexpression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) and ERK1/2 was detected in HCC, and that their activation was required for liver cancer cell proliferation and survival. In the present study, we determined the efficacy of a specific MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRAY-142886) in treatment of HCC. Treatment of primary HCC cells with AZD6244 led to growth inhibition, elevation of the cleavage of caspase-3 and caspase-7, and cleaved poly(ADP)ribose polymerase, but inhibition of ERK1/2 and p90RSK phosphorylation. Studying the protein expression profile of seven HCC xenografts revealed that their growth rate was positively correlated with the levels of phosphorylated MEK. AZD6244, when given p.o. to mice bearing these xenografts, resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth. AZD6244-induced growth suppression was associated with inactivation of ERK1/2 and p90RSK, and up-regulation of activated caspase-3 and caspase-7, and cleaved poly(ADP)ribose polymerase. Our data suggest that the MEK-ERK pathway plays an important role in the growth and survival of liver cancer cells and that the HCC xenograft models are excellent tools for screening preclinical drugs. Targeted inhibition of the MEK-ERK pathway with AZD6244 may represent an alternative approach for the treatment of this disease.
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2007
Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE: The Ras-Raf-mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) pathway is overactive in many human cancers and is thus a target for novel therapeutics. We have developed a highly potent and selective inhibitor of MEK1/2. The purpose of these studies has been to show the biological efficacy of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244) in enzymatic, cellular, and animal models. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: The ability of ARRY-142886 to inhibit purified MEK1 as well as other kinases was evaluated. Its effects on extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation and proliferation in several cell lines were also determined. Finally, the inhibitor was tested in HT-29 (colorectal) and BxPC3 (pancreatic) xenograft tumor models. RESULTS: The IC(50) of ARRY-142886 was determined to be 14 nmol/L against purified MEK1. This activity is not competitive with ATP, which is consistent with the high specificity of compound for MEK1/2. Basal and epidermal growth factor-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation was inhibited in several cell lines as well as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Treatment with ARRY-142886 resulted in the growth inhibition of several cell lines containing B-Raf and Ras mutations but had no effect on a normal fibroblast cell line. When dosed orally, ARRY-142886 was capable of inhibiting both ERK1/2 phosphorylation and growth of HT-29 xenograft tumors in nude mice. Tumor regressions were also seen in a BxPC3 xenograft model. In addition, tumors remained responsive to growth inhibition after a 7-day dosing holiday. CONCLUSIONS: ARRY-142886 is a potent and selective MEK1/2 inhibitor that is highly active in both in vitro and in vivo tumor models. This compound is currently being investigated in clinical studies.

 网站首页
网站首页