概要
• For Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (Catalog #70022) MNCs were cultured in MesenCult™ Proliferation Kit (Human; Catalog #05411)
• For Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Derived in ACF Medium (Catalog #70071) MNCs were cultured in MesenCult™-ACF Culture Kit (Catalog #05449)
Cells were obtained using Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved consent forms and protocols.
Certain products are only available in select territories. Please contact your local Sales representative or Product & Scientific Support at techsupport@stemcell.com for further information.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Primary Cells.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells, Frozen | 70022 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Derived in ACF Medium, Frozen | 70071 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
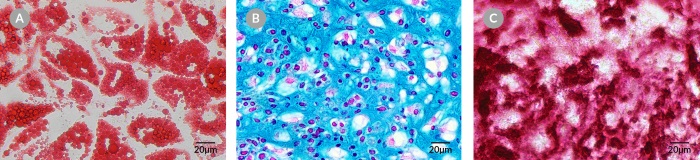
Figure 1. Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Cultured Using the MesenCult™-ACF Culture Kit Maintain Multi-Lineage Differentiation Potential
Human bone marrow stromal cells derived in ACF medium (Catalog #70071) using the MesenCult™-ACF Culture Kit (Catalog #05449) differentiate to A) adipocytes (Oil Red O staining), B) chondrocytes (Alcian Blue and Nuclear Fast Red staining) and C) osteoblasts (Alizarin Red S staining).

 网站首页
网站首页