概要
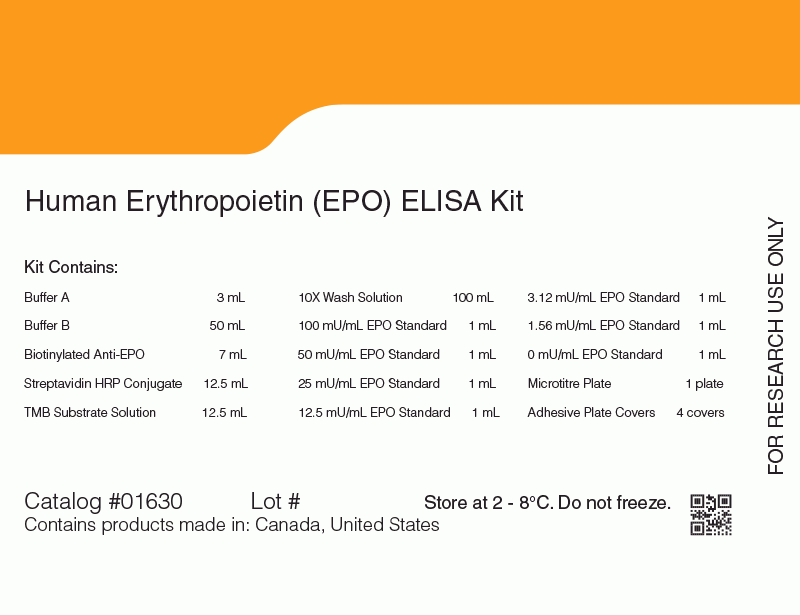
The glycoprotein EPO is the main physiological regulator of red blood cell formation. The EPO ELISA Kit is a rapid 3-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) designed for the quantitative measurement of natural and recombinant human EPO. The assay uses two monoclonal antibodies raised against human urinary EPO. These antibodies bind two non-overlapping epitopes on the EPO polypeptide and show high-affinity binding to both natural and recombinant EPO. The range of detection for the kit is 1.6 - 100 mU/mL. The EPO ELISA Kit has an assay time of approximately 3 hours.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | 16E68690 or higher | English |
| Manual | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 4 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 5 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 6 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 7 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 8 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 9 | Erythropoietin (EPO) ELISA Kit | 01630 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (4)
Lancet 2000 MAY
The blood in systemic disorders.
Abstract
Abstract
* The high rate of proliferation required of the bone marrow renders it highly susceptible to the influence of external factors. * Anaemia is the most common haematological abnormality seen in systemic disorders. * In the anaemia of chronic disease, erythropoietin production is reduced and proliferation of erythroid progenitor cells is also impaired; this anaemia can generally be alleviated by correction of the underlying disease process. * The status of the endocrine system must always be considered in evaluation of a normocytic, normochromic anaemia. * Anaemia in infection can be due to host or parasite factors or to the treatment administered. * Anaemia due to malignant disease responds to erythropoietin therapy in many cases; failure to respond is a poor prognostic sign.
Blood 1990 OCT
A specific in vitro bioassay for measuring erythropoietin levels in human serum and plasma.
Abstract
Abstract
The accurate measurement of biologically active erythropoietin (Ep) in human serum and plasma using present in vivo and in vitro bioassays is difficult because of the presence of both inhibitors and non-Ep stimulators of erythropoiesis. We have developed a simple procedure to quantitatively purify Ep from serum and plasma for subsequent testing in the phenylhydrazine-treated mouse spleen cell assay. The method involves absorption of Ep to an immobilized high-affinity anti-Ep monoclonal antibody and acid elution of the antibody-bound material. After neutralization, the eluted EP is then tested directly in the in vitro bioassay without interference by other serum proteins. By using magnetic beads as a solid support for the antibody, washing and elution steps can be performed rapidly and efficiently. Recoveries of Ep after this procedure show very little sample-to-sample variation and are consistently between 45% and 55%, which is close to the maximum binding expected for the anti-Ep antibody. Coupled with the 7.4-fold concentration that this procedure affords, there is an overall increase in sensitivity of three- to fourfold, which makes this assay suitable for accurately measuring Ep levels in patients with below-average titers. Results with this magnetic bead assay indicate that accurate and reproducible estimates for Ep levels in the serum and plasma from healthy donors as well as from patients with hematologic disorders can be obtained. Titers of biologically active Ep in the sera from a group of patients with either leukemia or lymphoma were found to be elevated, and the values correlated well with titers of immunoreactive Ep measured in the Ep radioimmunoassay. Because of its specificity and high sensitivity, the magnetic bead assay is a valuable alternative to immunoassays for the measurement of elevated, normal, and even subnormal Ep levels in human serum and plasma.
Experimental hematology 1990 MAR
Immunochemical analysis of monoclonal antibodies to human erythropoietin.
Abstract
Abstract
We recently reported the development of three monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) to biologically active human erythropoietin (Ep). In the present study, we investigated the epitope specificity of these three antibodies, as well as their reactivity with Eps derived from species other than man. All three antibodies reacted with the Ep polypeptide itself, rather than with its carbohydrate moieties. Moreover, all three antibodies recognized separate nonoverlapping epitopes. Further studies with reduced/alkylated Ep and with sodium dodecyl sulfate-denatured Ep suggested that two of the MoAbs, anti-Ep-2 and anti-Ep-16, were specific for conformational, nonlinear determinants on the Ep molecule, whereas the third MoAb, anti-Ep-26, appeared to recognize a linear epitope. However, anti-Ep-26 did not react with synthetic peptides representing the 26 amino-, the 99-129 mid-region, or the 10 carboxy-terminal residues of Ep, nor with trypsin-, chymotrypsin-, or V8 protease-digested fragments of Ep. When tested with Ep from different species, the neutralizing capabilities of the three MoAbs were clearly different. Comparing their effectiveness against baboon, ovine and murine Ep, antibody 2 was most effective at neutralizing baboon Ep, antibody 16 was most effective against murine Ep, and antibody 26 showed little reactivity with any of these nonhuman Eps. Because these various Eps readily stimulate across species barriers, it is likely that the receptor binding domain on Ep has remained relatively conserved during evolution. Our results therefore suggest that the neutralizing capacity of our three anti-Ep MoAbs is caused not by binding directly to the Ep receptor binding domain on Ep, but by binding to distant regions, causing conformational changes in Ep, or by binding to regions close to the binding site, steric hindrance.
Blood 1990 AUG
Detection and isolation of the erythropoietin receptor using biotinylated erythropoietin.
Abstract
Abstract
Procedures have been developed to label human erythropoietin (Ep) with biotin to detect and isolate the Ep-receptor. The labeling method used the abundant carbohydrate groups on Ep and resulted in biologically active biotin-Ep (b-Ep) containing 8 to 10 biotins per Ep molecule. Specific binding of b-Ep to cells from spleens of mice made anemic by phenylhydrazine injections was demonstrated using 125I-labeled streptavidin. B-Ep, together with fluorescently tagged streptavidin, was found to specifically detect Ep-receptor-bearing cells by flow cytometry. This was demonstrated in several ways. First, approximately 90% of nucleated spleen cells from phenylhydrazine-treated mice were clearly fluorescent after staining with b-Ep and streptavidin-phycoerythrin, whereas only background fluorescence was detected using spleen cells from untreated mice. In addition, Ep-receptors were detected on 5% to 10% of normal mouse bone marrow cells, and these cells could be identified as erythroid in nature by separating the cells into subpopulations based on light-scatter properties. Third, Ep-receptor expression was found to correlate positively with expression of transferrin receptors, confirming the erythroid nature of these cells. B-Ep was also used to isolate Ep-receptors from monkey COS cells transfected with the murine Ep-receptor cDNA. In these experiments a cell-surface-bound protein of approximately 65 Kd and an intracellular protein of approximately 60 Kd were isolated from these cells. The procedures described in this report for detecting Ep-receptor expressing cells and for isolating the Ep-receptor should be valuable for purifying erythroid cells from heterogeneous cell populations, for elucidating the structure of the Ep-receptor, and for studying the biological activities of Ep at the cellular and molecular level.

 网站首页
网站首页