概要
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Human Recombinant MCP-1 (CCL2) | 78087, 78087.1 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Human Recombinant MCP-1 (CCL2) | 78087.1 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
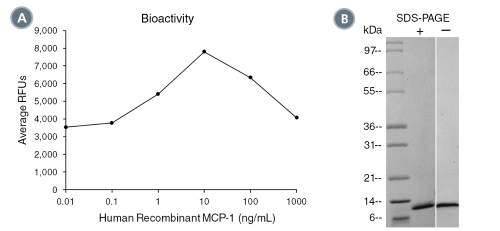
(A) The biological activity of Human Recombinant MCP-1 was tested by its ability to induce chemotaxis of THP-1 cells. Cell migration was measured after 1 hour using a fluorometric assay method. Increase in migration over basal level was seen starting at 1 ng/mL. (B) 1 μg of Human Recombinant MCP-1 was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (+) and non-reducing (-) conditions and visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. Human Recombinant MCP-1 has a predicted molecular mass of 8.7 kDa.

 网站首页
网站首页