概要
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Human Recombinant IFN-beta | 78113, 78113.1 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Human Recombinant IFN-beta | 78113, 78113.1 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
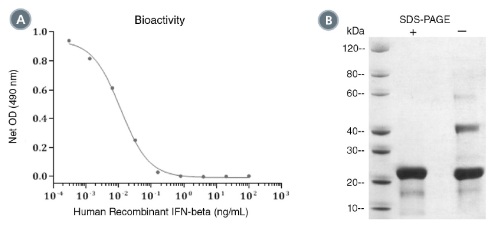
(A) The biological activity of Human Recombinant IFN-beta was tested by its ability to inhibit the proliferation of TF-1 cells. Cell proliferation was measured using a fluorometric assay method. The EC50 is defined as the effective concentration of the growth factor at which cell proliferation is at 50% of maximum. The EC50 in the above example is less than 0.1 ng/mL. (B) 2 μg of Human Recombinant IFN-beta was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (+) and non-reducing (-) conditions and visualized by Coomassie Blue staining.

 网站首页
网站首页