概要
The EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate B cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with biotinylated antibodies directed against non-B cells and streptavidin-coated magnetic particles (RapidSpheres™ ). Labeled cells are separated using and EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
For isolation of B cells expressing CD11b or CD43, we recommend using the EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation kit (Catalog #19844).
This product replaces the EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19754) for even faster cell isolations.
For isolation of B cells expressing CD11b or CD43, we recommend using the EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation kit (Catalog #19844).
This product replaces the EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19754) for even faster cell isolations.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit | 19854RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
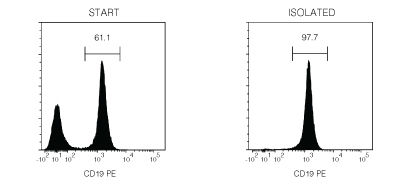
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with mouse splenocytes, the B cell content of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 94 - 98%.
Publications (30)
Nature nanotechnology 2020 jun
Role of nanoscale antigen organization on B-cell activation probed using DNA origami.
Abstract
Abstract
Vaccine efficacy can be increased by arraying immunogens in multivalent form on virus-like nanoparticles to enhance B-cell activation. However, the effects of antigen copy number, spacing and affinity, as well as the dimensionality and rigidity of scaffold presentation on B-cell activation remain poorly understood. Here, we display the clinical vaccine immunogen eOD-GT8, an engineered outer domain of the HIV-1 glycoprotein-120, on DNA origami nanoparticles to systematically interrogate the impact of these nanoscale parameters on B-cell activation in vitro. We find that B-cell signalling is maximized by as few as five antigens maximally spaced on the surface of a 40-nm viral-like nanoparticle. Increasing antigen spacing up to {\~{}}25-30 nm monotonically increases B-cell receptor activation. Moreover, scaffold rigidity is essential for robust B-cell triggering. These results reveal molecular vaccine design principles that may be used to drive functional B-cell responses.
Nature biomedical engineering 2020 jun
Pharmacokinetic tuning of protein-antigen fusions enhances the immunogenicity of T-cell vaccines.
Abstract
Abstract
The formulations of peptide-based antitumour vaccines being tested in clinical studies are generally associated with weak potency. Here, we show that pharmacokinetically tuning the responses of peptide vaccines by fusing the peptide epitopes to carrier proteins optimizes vaccine immunogenicity in mice. In particular, we show in immunized mice that the carrier protein transthyretin simultaneously optimizes three factors: efficient antigen uptake in draining lymphatics from the site of injection, protection of antigen payloads from proteolytic degradation and reduction of antigen presentation in uninflamed distal lymphoid organs. Optimizing these factors increases vaccine immunogenicity by up to 90-fold and maximizes the responses to viral antigens, tumour-associated antigens, oncofetal antigens and shared neoantigens. Protein-peptide epitope fusions represent a facile and generalizable strategy for enhancing the T-cell responses elicited by subunit vaccines.
Scientific reports 2020 jul
Bioluminescence for in vivo detection of cell-type-specific inflammation in a mouse model of uveitis.
Abstract
Abstract
This study reports the use of cell-type-specific in vivo bioluminescence to measure intraocular immune cell population dynamics during the course of inflammation in a mouse model of uveitis. Transgenic lines expressing luciferase in inflammatory cell subsets (myeloid cells, T cells, and B cells) were generated and ocular bioluminescence was measured serially for 35 days following uveitis induction. Ocular leukocyte populations were identified using flow cytometry and compared to the ocular bioluminescence profile. Acute inflammation is neutrophilic (75{\%} of ocular CD45 + cells) which is reflected by a significant increase in ocular bioluminescence in one myeloid reporter line on day 2. By day 7, the ocular T cell population increases to 50{\%} of CD45 + cells, leading to a significant increase in ocular bioluminescence in the T cell reporter line. While initially negligible ({\textless} 1{\%} of CD45 + cells), the ocular B cell population increases to {\textgreater} 4{\%} by day 35. This change is reflected by a significant increase in the ocular bioluminescence of the B cell reporter line starting on day 28. Our data demonstrates that cell-type-specific in vivo bioluminescence accurately detects changes in multiple intraocular immune cell populations over time in experimental uveitis. This assay could also be useful in other inflammatory disease models.
Frontiers in immunology 2020
Missing-in-Metastasis/Metastasis Suppressor 1 Regulates B Cell Receptor Signaling, B Cell Metabolic Potential, and T Cell-Independent Immune Responses.
Abstract
Abstract
Efficient generation of antibodies by B cells is one of the prerequisites of protective immunity. B cell activation by cognate antigens via B cell receptors (BCRs), or pathogen-associated molecules through pattern-recognition receptors, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), leads to transcriptional and metabolic changes that ultimately transform B cells into antibody-producing plasma cells or memory cells. BCR signaling and a number of steps downstream of it rely on coordinated action of cellular membranes and the actin cytoskeleton, tightly controlled by concerted action of multiple regulatory proteins, some of them exclusive to B cells. Here, we dissect the role of Missing-In-Metastasis (MIM), or Metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1), a cancer-associated membrane and actin cytoskeleton regulating protein, in B cell-mediated immunity by taking advantage of MIM knockout mouse strain. We show undisturbed B cell development and largely normal composition of B cell compartments in the periphery. Interestingly, we found that MIM-/- B cells are defected in BCR signaling in response to surface-bound antigens but, on the other hand, show increased metabolic activity after stimulation with LPS or CpG. In vivo, MIM knockout animals exhibit impaired IgM antibody responses to immunization with T cell-independent antigen. This study provides the first comprehensive characterization of MIM in B cells, demonstrates its regulatory role for B cell-mediated immunity, as well as proposes new functions for MIM in tuning receptor signaling and cellular metabolism, processes, which may also contribute to the poorly understood functions of MIM in cancer.
Science advances 2020
B cell Sirt1 deacetylates histone and non-histone proteins for epigenetic modulation of AID expression and the antibody response.
Abstract
Abstract
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) mediates immunoglobulin class switch DNA recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM), critical processes for maturation of the antibody response. Epigenetic factors, such as histone deacetylases (HDACs), would underpin B cell differentiation stage-specific AID expression. Here, we showed that NAD+-dependent class III HDAC sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) is highly expressed in resting B cells and down-regulated by stimuli inducing AID. B cell Sirt1 down-regulation, deprivation of NAD+ cofactor, or genetic Sirt1 deletion reduced deacetylation of Aicda promoter histones, Dnmt1, and nuclear factor-$\kappa$B (NF-$\kappa$B) p65 and increased AID expression. This promoted class-switched and hypermutated T-dependent and T-independent antibody responses or led to generation of autoantibodies. Genetic Sirt1 overexpression, Sirt1 boost by NAD+, or allosteric Sirt1 enhancement by SRT1720 repressed AID expression and CSR/SHM. By deacetylating histone and nonhistone proteins (Dnmt1 and NF-$\kappa$B p65), Sirt1 transduces metabolic cues into epigenetic changes to play an important B cell-intrinsic role in modulating antibody and autoantibody responses.
Nature communications 2020
B cell-intrinsic epigenetic modulation of antibody responses by dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids.
Abstract
Abstract
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) butyrate and propionate are metabolites from dietary fiber's fermentation by gut microbiota that can affect differentiation or functions of T cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. We show here that at low doses these SCFAs directly impact B cell intrinsic functions to moderately enhance class-switch DNA recombination (CSR), while decreasing at higher doses over a broad physiological range, AID and Blimp1 expression, CSR, somatic hypermutation and plasma cell differentiation. In human and mouse B cells, butyrate and propionate decrease B cell Aicda and Prdm1 by upregulating select miRNAs that target Aicda and Prdm1 mRNA-3'UTRs through inhibition of histone deacetylation (HDAC) of those miRNA host genes. By acting as HDAC inhibitors, not as energy substrates or through GPR-engagement signaling in these B cell-intrinsic processes, these SCFAs impair intestinal and systemic T-dependent and T-independent antibody responses. Their epigenetic impact on B cells extends to inhibition of autoantibody production and autoimmunity in mouse lupus models.

 网站首页
网站首页