概要
The EasySep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit is designed to isolate T cells from fresh or previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-T cells and dextran-coated magnetic particles. The labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human T Cell Isolation Kit (17951) which isolates cells in just 8 minutes.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human T Cell Isolation Kit (17951) which isolates cells in just 8 minutes.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit | 19051 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19051RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit | 19051 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit | 19051 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19051RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19051RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
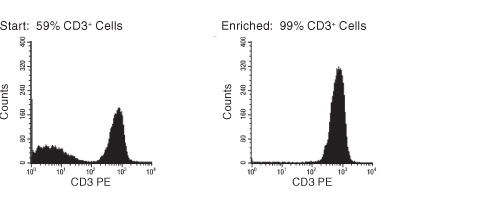
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results With EasySep™ Human T Cell Enrichment Kit
Starting with previously frozen mononuclear cells, the CD3+ cell content of the enriched fraction typically ranges from 95% - 99%.
Publications (14)
Nature chemical biology 2019 mar
An allosteric MALT1 inhibitor is a molecular corrector rescuing function in an immunodeficient patient.
Abstract
Abstract
MALT1 paracaspase is central for lymphocyte antigen-dependent responses including NF-kappaB activation. We discovered nanomolar, selective allosteric inhibitors of MALT1 that bind by displacing the side chain of Trp580, locking the protease in an inactive conformation. Interestingly, we had previously identified a patient homozygous for a MALT1 Trp580-to-serine mutation who suffered from combined immunodeficiency. We show that the loss of tryptophan weakened interactions between the paracaspase and C-terminal immunoglobulin MALT1 domains resulting in protein instability, reduced protein levels and functions. Upon binding of allosteric inhibitors of increasing potency, we found proportionate increased stabilization of MALT1-W580S to reach that of wild-type MALT1. With restored levels of stable MALT1 protein, the most potent of the allosteric inhibitors rescued NF-kappaB and JNK signaling in patient lymphocytes. Following compound washout, MALT1 substrate cleavage was partly recovered. Thus, a molecular corrector rescues an enzyme deficiency by substituting for the mutated residue, inspiring new potential precision therapies to increase mutant enzyme activity in other deficiencies.
Science immunology 2019 feb
Multifactorial heterogeneity of virus-specific T cells and association with the progression of human chronic hepatitis B infection.
Abstract
Abstract
Associations between chronic antigen stimulation, T cell dysfunction, and the expression of various inhibitory receptors are well characterized in several mouse and human systems. During chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (CHB), T cell responses are blunted with low frequencies of virus-specific T cells observed, making these parameters difficult to study. Here, using mass cytometry and a highly multiplexed combinatorial peptide-major histocompatibility complex (pMHC) tetramer strategy that allows for the detection of rare antigen-specific T cells, we simultaneously probed 484 unique HLA-A*1101-restricted epitopes spanning the entire HBV genome on T cells from patients at various stages of CHB. Numerous HBV-specific T cell populations were detected, validated, and profiled. T cells specific for two epitopes (HBVpol387 and HBVcore169) displayed differing and complex heterogeneities that were associated with the disease progression, and the expression of inhibitory receptors on these cells was not linearly related with their extent of T cell dysfunction. For HBVcore169-specific CD8+ T cells, we found cellular markers associated with long-term memory, polyfunctionality, and the presence of several previously unidentified public TCR clones that correlated with viral control. Using high-dimensional trajectory analysis of these cellular phenotypes, a pseudo-time metric was constructed that fit with the status of viral infection in corresponding patients. This was validated in a longitudinal cohort of patients undergoing antiviral therapy. Our study uncovers complex relationships of inhibitory receptors between the profiles of antigen-specific T cells and the status of CHB with implications for new strategies of therapeutic intervention.
Cancer research 2017 NOV
PD-1 Status in CD8+ T Cells Associates with Survival and Anti-PD-1 Therapeutic Outcomes in Head and Neck Cancer.
Abstract
Abstract
Improved understanding of expression of immune checkpoint receptors (ICR) on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) may facilitate more effective immunotherapy in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients. A higher frequency of PD-1+ TIL has been reported in human papillomavirus (HPV)+ HNC patients, despite the role of PD-1 in T-cell exhaustion. This discordance led us to hypothesize that the extent of PD-1 expression more accurately defines T-cell function and prognostic impact, because PD-1high T cells may be more exhausted than PD-1low T cells and may influence clinical outcome and response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. In this study, PD-1 expression was indeed upregulated on HNC patient TIL, and the frequency of these PD-1+ TIL was higher in HPV+ patients (P = 0.006), who nonetheless experienced significantly better clinical outcome. However, PD-1high CD8+ TILs were more frequent in HPV- patients and represented a more dysfunctional subset with compromised IFN-γ secretion. Moreover, HNC patients with higher frequencies of PD-1high CD8+ TIL showed significantly worse disease-free survival and higher hazard ratio for recurrence (P < 0.001), while higher fractions of PD-1low T cells associated with HPV positivity and better outcome. In a murine HPV+ HNC model, anti-PD-1 mAb therapy differentially modulated PD-1high/low populations, and tumor rejection associated with loss of dysfunctional PD-1high CD8+ T cells and a significant increase in PD-1low TIL. Thus, the extent of PD-1 expression on CD8+ TIL provides a potential biomarker for anti-PD-1-based immunotherapy. Cancer Res; 77(22); 6353-64. textcopyright2017 AACR.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2016 MAY
The Complement Inhibitor Factor H Generates an Anti-Inflammatory and Tolerogenic State in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
The activation of the complement system is a key initiating step in the protective innate immune-inflammatory response against injury, although it may also cause harm if left unchecked. The structurally related soluble complement inhibitors C4b-binding protein (C4BP) and factor H (FH) exert a tight regulation of the classical/lectin and alternative pathways of complement activation, respectively, attenuating the activity of the C3/C5 convertases and, consequently, avoiding serious damage to host tissues. We recently reported that the acute-phase C4BP isoform C4BP lacking the β-chain plays a pivotal role in the modulation of the adaptive immune responses. In this study, we demonstrate that FH acts in the early stages of monocyte to dendritic cell (DC) differentiation and is able to promote a distinctive tolerogenic and anti-inflammatory profile on monocyte-derived DCs (MoDCs) challenged by a proinflammatory stimulus. Accordingly, FH-treated and LPS-matured MoDCs are characterized by altered cytoarchitecture, resembling immature MoDCs, lower expression of the maturation marker CD83 and the costimulatory molecules CD40, CD80, and CD86, decreased production of key proinflammatory Th1-cytokines (IL-12, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-8), and preferential production of immunomodulatory mediators (IL-10 and TGF-β). Moreover, FH-treated MoDCs show low Ag uptake and, when challenged with LPS, display reduced CCR7 expression and chemotactic migration, impaired CD4(+) T cell alloproliferation, inhibition of IFN-γ secretion by the allostimulated T cells, and, conversely, induction of CD4(+)CD127(low/negative)CD25(high)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Thus, this novel noncanonical role of FH as an immunological brake able to directly affect the function of MoDCs in an inflammatory environment may exhibit therapeutic potential in hypersensitivity, transplantation, and autoimmunity.
Leukemia 2015 JAN
A multiepitope of XBP1, CD138 and CS1 peptides induces myeloma-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in T cells of smoldering myeloma patients.
Abstract
Abstract
We evaluated a cocktail of HLA-A2-specific peptides including heteroclitic XBP1 US184-192 (YISPWILAV), heteroclitic XBP1 SP367-375 (YLFPQLISV), native CD138260-268 (GLVGLIFAV) and native CS1239-247 (SLFVLGLFL), for their ability to elicit multipeptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (MP-CTLs) using T cells from smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) patients. Our results demonstrate that MP-CTLs generated from SMM patients' T cells show effective anti-MM responses including CD137 (4-1BB) upregulation, CTL proliferation, interferon-γ production and degranulation (CD107a) in an HLA-A2-restricted and peptide-specific manner. Phenotypically, we observed increased total CD3(+)CD8(+) T cells (textgreater80%) and cellular activation (CD69(+)) within the memory SMM MP-CTL (CD45RO(+)/CD3(+)CD8(+)) subset after repeated multipeptide stimulation. Importantly, SMM patients could be categorized into distinct groups by their level of MP-CTL expansion and antitumor activity. In high responders, the effector memory (CCR7(-)CD45RO(+)/CD3(+)CD8(+)) T-cell subset was enriched, whereas the remaining responders' CTL contained a higher frequency of the terminal effector (CCR7(-)CD45RO(-)/CD3(+)CD8(+)) subset. These results suggest that this multipeptide cocktail has the potential to induce effective and durable memory MP-CTL in SMM patients. Therefore, our findings provide the rationale for clinical evaluation of a therapeutic vaccine to prevent or delay progression of SMM to active disease.
The Journal of Immunology 2014
Human NK Cells Licensed by Killer Ig Receptor Genes Have an Altered Cytokine Program That Modifies CD4+ T Cell Function
Abstract
Abstract
NK cells are innate immune cells known for their cytolytic activities toward tumors and infections. They are capable of expressing diverse killer Ig-like receptors (KIRs), and KIRs are implicated in susceptibility to Crohn's disease (CD), a chronic intestinal inflammatory disease. However, the cellular mechanism of this genetic contribution is unknown. In this study, we show that the licensing" of NK cells�

 网站首页
网站首页