概要
The EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate naive CD4+ T cells from fresh or previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing CD8, CD14, CD16, CD19, CD20, CD25, CD36, CD56, CD61, CD66b, CD123, HLA-DR, TCRγ/δ, glycophorin A, and dextran-coated magnetic particles. CD45RO+ cells are targeted for removal with a biotinylated anti-CD45RO antibody, and a bispecific Tetrameric Antibody Complex that recognizes biotin and dextran. The labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit II (17555) which isolates cells in just 11 minutes.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit II (17555) which isolates cells in just 11 minutes.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19555RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
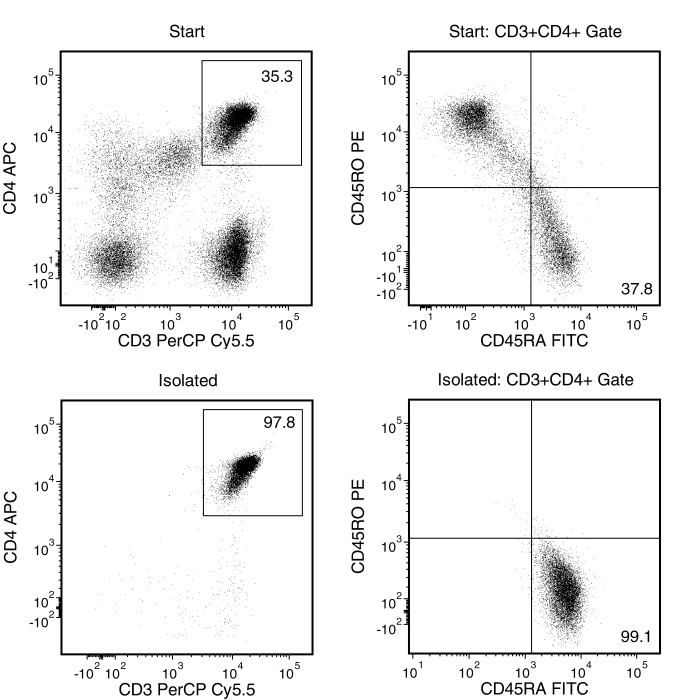
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with a single-cell suspension of PBMCs, the naïve CD4+ T cell (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CD45RO-) content of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 91.3% - 96.9%. In the example above, the purities of the start and isolated fraction are 11.1% and 93.2%, respectively.
Publications (2)
Cell reports 2020 feb
Nef-Mediated CD3-TCR Downmodulation Dampens Acute Inflammation and Promotes SIV Immune Evasion.
Abstract
Abstract
The inability of Nef to downmodulate the CD3-T cell receptor (TCR) complex distinguishes HIV-1 from other primate lentiviruses and may contribute to its high virulence. However, the role of this Nef function in virus-mediated immune activation and pathogenicity remains speculative. Here, we selectively disrupted this Nef activity in SIVmac239 and analyzed the consequences for the virological, immunological, and clinical outcome of infection in rhesus macaques. The inability to downmodulate CD3-TCR does not impair viral replication during acute infection but is associated with increased immune activation and antiviral gene expression. Subsequent early reversion in three of six animals suggests strong selective pressure for this Nef function and is associated with high viral loads and progression to simian AIDS. In the absence of reversions, however, viral replication and the clinical course of infection are attenuated. Thus, Nef-mediated downmodulation of CD3 dampens the inflammatory response to simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection and seems critical for efficient viral immune evasion.
Scientific Reports 2016 FEB
Staphylococcus aureus-derived factors induce IL-10, IFN-γ and IL-17A-expressing FOXP3(+)CD161(+) T-helper cells in a partly monocyte-dependent manner.
Abstract
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a human pathogen as well as a frequent colonizer of skin and mucosa. This bacterium potently activates conventional T-cells through superantigens and it is suggested to induce T-cell cytokine-production as well as to promote a regulatory phenotype in T-cells in order to avoid clearance. This study aimed to investigate how S. aureus impacts the production of regulatory and pro-inflammatory cytokines and the expression of CD161 and HELIOS by peripheral CD4(+)FOXP3(+) T-cells. Stimulation of PBMC with S. aureus 161:2-cell free supernatant (CFS) induced expression of IL-10, IFN-γ and IL-17A in FOXP3(+) cells. Further, CD161 and HELIOS separated the FOXP3(+) cells into four distinct populations regarding cytokine-expression. Monocyte-depletion decreased S. aureus 161:2-induced activation of FOXP3(+) cells while pre-stimulation of purified monocytes with S. aureus 161:2-CFS and subsequent co-culture with autologous monocyte-depleted PBMC was sufficient to mediate activation of FOXP3(+) cells. Together, these data show that S. aureus potently induces FOXP3(+) cells and promotes a diverse phenotype with expression of regulatory and pro-inflammatory cytokines connected to increased CD161-expression. This could indicate potent regulation or a contribution of FOXP3(+) cells to inflammation and repression of immune-suppression upon encounter with S. aureus.

 网站首页
网站首页