概要
The EasySep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate gamma/delta T cells from fresh or previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-gamma/delta T cells and dextran-coated magnetic particles. The labeled cells are separated using the EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. The desired cells are poured off into a new tube. To obtain a custom kit optimized for culture-expanded PBMCs, contact STEMCELL Technologies’ Technical Support at techsupport@stemcell.com.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Kit | 19255 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Kit | 19255RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | EasySep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Kit | 19255 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Kit | 19255RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
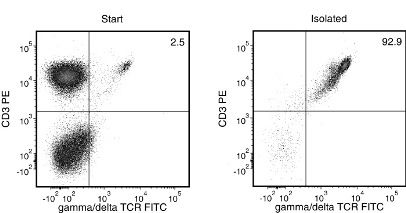
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Human Gamma/Delta T Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with fresh PBMCs, the gamma/delta TCR+CD3+ cell content of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 90 - 97%. In the above example, the purities of the start and final isolated fractions are 2.5% and 92.9%, respectively.
Publications (1)
Nature chemical biology 2020 dec
Targeted glycan degradation potentiates the anticancer immune response in vivo.
Abstract
Abstract
Currently approved immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies targeting the PD-1 and CTLA-4 receptor pathways are powerful treatment options for certain cancers; however, most patients across cancer types still fail to respond. Consequently, there is interest in discovering and blocking alternative pathways that mediate immune suppression. One such mechanism is an upregulation of sialoglycans in malignancy, which has been recently shown to inhibit immune cell activation through multiple mechanisms and therefore represents a targetable glycoimmune checkpoint. Since these glycans are not canonically druggable, we designed an $\alpha$HER2 antibody-sialidase conjugate that potently and selectively strips diverse sialoglycans from breast cancer cells. In syngeneic breast cancer models, desialylation enhanced immune cell infiltration and activation and prolonged the survival of mice, an effect that was dependent on expression of the Siglec-E checkpoint receptor found on tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells. Thus, antibody-sialidase conjugates represent a promising modality for glycoimmune checkpoint therapy.

 网站首页
网站首页