概要
Isolate highly purified CD34+ cells from fresh whole umbilical cord blood using a simple, two-step procedure. First, hematopoietic progenitor cells are pre-enriched using the RosetteSep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Pre-Enrichment Cocktail (15896C) with antibodies recognizing T cell, B cell, myeloid cell and platelet surface markers. CD34+ cells are then selected using the EasySep™ Human CD34 Positive Selection Cocktail (18096C), which contains an antibody recognizing CD34.
If isolating CD34+ cells from fresh blood or buffy coat the Complete Kit for Human Whole Blood CD34+ Cells (Catalog #15086) is recommended.
If isolating CD34+ cells from other samples, including fresh or previously frozen mobilized peripheral blood or bone marrow mononuclear cells, or from previously frozen cord blood mononuclear cells, we recommend using the EasySep™ Human CD34 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #17856).
This product replaces the stand alone EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18096).
If isolating CD34+ cells from fresh blood or buffy coat the Complete Kit for Human Whole Blood CD34+ Cells (Catalog #15086) is recommended.
If isolating CD34+ cells from other samples, including fresh or previously frozen mobilized peripheral blood or bone marrow mononuclear cells, or from previously frozen cord blood mononuclear cells, we recommend using the EasySep™ Human CD34 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #17856).
This product replaces the stand alone EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18096).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human CB CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human CB CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human CB CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Human CB CD34 Positive Selection Kit II | 17896RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
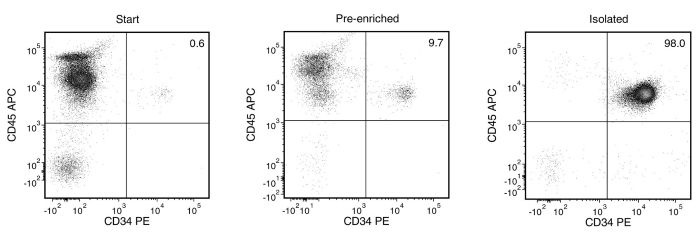
Figure 1. EasySep™ Human Cord Blood CD34 Positive Selection Kit II
Starting with fresh cord blood, the CD34+ cell content of the isolated fraction is typically 91 ± 9% (mean ± SD using the purple EasySep™ Magnet).
Publications (2)
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2020 feb
Discovery of Berberine that Targetedly Induces Autophagic Degradation of both BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL T315I through Recruiting LRSAM1 for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE Imatinib, the breakpoint cluster region protein (BCR)/Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog (ABL) inhibitor, is widely used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, imatinib resistance develops in many patients. Therefore, new drugs with improved therapeutic effects are urgently needed. Berberine (BBR) is a potent BCR-ABL inhibitor for imatinib-sensitive and -resistant CML. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN Protein structure analysis and virtual screening were used to identify BBR targets in CML. Molecular docking analysis, surface plasmon resonance imaging, nuclear magnetic resonance assays, and thermoshift assays were performed to confirm the BBR target. The change in BCR-ABL protein expression after BBR treatment was assessed by Western blotting. The effects of BBR were assessed in vitro in cell lines, in vivo in mice, and in human CML bone marrow cells as a potential strategy to overcome imatinib resistance. RESULTS We discovered that BBR bound to the protein tyrosine kinase domain of BCR-ABL. BBR inhibited the activity of BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL with the T315I mutation, and it also degraded these proteins via the autophagic lysosome pathway by recruiting E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase LRSAM1. BBR inhibited the cell viability and colony formation of CML cells and prolonged survival in CML mouse models with imatinib sensitivity and resistance. CONCLUSIONS The results show that BBR directly binds to and degrades BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL T315I via the autophagic lysosome pathway by recruiting LRSAM1. The use of BBR is a new strategy to improve the treatment of patients with CML with imatinib sensitivity or resistance.
Nature Biotechnology 2016 APR
Directed evolution of a recombinase that excises the provirus of most HIV-1 primary isolates with high specificity.
Abstract
Abstract
Current combination antiretroviral therapies (cART) efficiently suppress HIV-1 reproduction in humans, but the virus persists as integrated proviral reservoirs in small numbers of cells. To generate an antiviral agent capable of eradicating the provirus from infected cells, we employed 145 cycles of substrate-linked directed evolution to evolve a recombinase (Brec1) that site-specifically recognizes a 34-bp sequence present in the long terminal repeats (LTRs) of the majority of the clinically relevant HIV-1 strains and subtypes. Brec1 efficiently, precisely and safely removes the integrated provirus from infected cells and is efficacious on clinical HIV-1 isolates in vitro and in vivo, including in mice humanized with patient-derived cells. Our data suggest that Brec1 has potential for clinical application as a curative HIV-1 therapy.

 网站首页
网站首页