概要
This kit targets non-naïve B cells for removal with antibodies recognizing specific surface markers. Unwanted cells are labeled with antibodies and EasySep™ Direct RapidSpheres™, and separated using an EasySep™ magnet. Desired cells are simply collected into a new tube and are immediately available for downstream applications such as flow cytometry, culture or DNA/RNA extraction.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Direct Human Naïve B Cell Isolation Kit | 19264 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Direct Human Naïve B Cell Isolation Kit | 19264 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Direct Human Naïve B Cell Isolation Kit | 19264 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
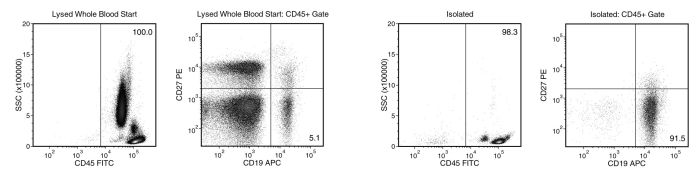
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Direct Human Naïve B Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with human whole blood from normal healthy donors, the typical naïve B cell (CD19+CD27-) content of the non-lysed final isolated fraction is 91.8 ± 3.6% (gated on CD45) or 82.4 ± 12.6% (not gated on CD45). In the above example, the naïve B cell (CD19+CD27-) content of the lysed whole blood start sample and non-lysed final isolated fraction is 5.1% and 91.5% (gated on CD45), respectively, or 5.1% and 90.0% (not gated on CD45), respectively. The starting frequency of naïve B cells in the non-lysed whole blood start sample above is 0.009% (data not shown).

 网站首页
网站首页