概要
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Direct Human CTC Enrichment Kit | 19657 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Direct Human CTC Enrichment Kit | 19657 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Direct Human CTC Enrichment Kit | 19657 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
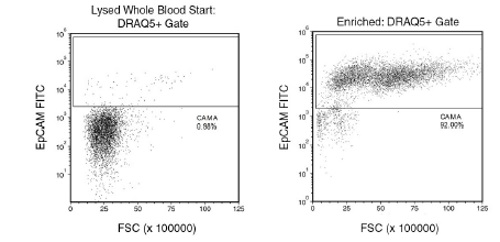
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Direct Human CTC Enrichment Profile
Starting with human whole blood from healthy donors, spiked with approximately 1% of CAMA cells (epithelial tumor cell line), the typical CTC (epithelial cell+) content of non-lysed final enriched fraction is 79 ± 16 % (using the silver “Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet; gated on DRAQ5™ for nucleated cells). Typically the log depletion of targeted CD45+ cells is 2.8 to 3.2. In the above example, CAMA cells were seeded into whole blood at a starting frequency of 0.98%. The CAMA cell (epithelial cell+) content of the enriched fraction is 92.02% with a 3.8 log depletion of CD45+ cells.

 网站首页
网站首页