概要
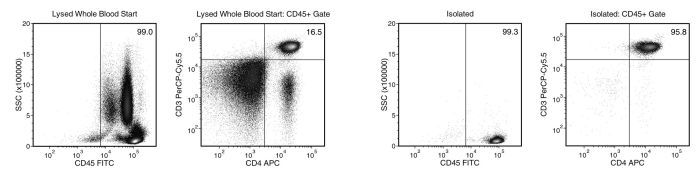
Isolate CD4+ T cells directly from human whole blood by immunomagnetic negative selection. Desired cells undergo minimal manipulation and are untouched and highly purified.
This product labels RBCs, platelets and unwanted cells with antibody complexes and magnetic particles. The magnetically labeled RBCs, platelets and non-target cells are separated from the untouched CD4+ T cells in an EasySep™ magnet and poured or pipetted into a new tube.
Isolated cells are available for use in downstream uses such as flow cytometry, functional assays or culture.
数据及文献
Publications (3)
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2019 sep
Multispecific Targeting with Synthetic Ankyrin Repeat Motif Chimeric Antigen Receptors.
A. Balakrishnan et al.
Abstract
PURPOSE The outgrowth of antigen-negative variants is a significant challenge for adoptive therapy with T cells that target a single specificity. Chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) are typically designed with one or two scFvs that impart antigen specificity fused to activation and costimulation domains of T-cell signaling molecules. We designed and evaluated the function of CARs with up to three specificities for overcoming tumor escape using Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins (DARPins) rather than scFvs for tumor recognition. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN A monospecific CAR was designed with a DARPin binder (E01) specific for EGFR and compared with a CAR designed using an anti-EGFR scFv. CAR constructs in which DARPins specific for EGFR, EpCAM, and HER2 were linked together in a single CAR were then designed and optimized to achieve multispecific tumor recognition. The efficacy of CAR-T cells bearing a multispecific DARPin CAR for treating tumors with heterogeneous antigen expression was evaluated in vivo. RESULTS The monospecific anti-EGFR E01 DARPin conferred potent tumor regression against EGFR+ targets that was comparable with an anti-EGFR scFv CAR. Linking three separate DARPins in tandem was feasible and in an optimized format generated a single tumor recognition domain that targeted a mixture of heterogeneous tumor cells, each expressing a single antigen, and displayed synergistic activity when tumor cells expressed more than one target antigen. CONCLUSIONS DARPins can serve as high-affinity recognition motifs for CAR design, and their robust architecture enables linking of multiple binders against different antigens to achieve functional synergy and reduce antigen escape.
Science signaling 2018 MAY
Tuning ITAM multiplicity on T cell receptors can control potency and selectivity to ligand density.
J. R. James
Abstract
The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) recognizes peptides from pathogenic proteins bound in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). To convert this binding event into downstream signaling, the TCR complex contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) that act as docking sites for the cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase ZAP-70. Unique among antigen receptors, the TCR complex uses 10 ITAMs to transduce peptide-MHC binding to the cell interior. Using synthetic, drug-inducible receptor-ligand pairs, it was found that greater ITAM multiplicity primarily enhanced the efficiency with which ligand binding was converted into an intracellular signal. This manifested as an increase in the fraction of cells that became activated in response to antigen, and a more synchronous initiation of TCR-proximal signaling, rather than direct amplification of the intracellular signals. Exploiting these findings, the potency and selectivity of chimeric antigen receptors targeted against cancer were substantially enhanced by modulating the number of encoded ITAMs.
Nature genetics 2016 DEC
A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies a restricted set of HIV host dependency factors.
Park RJ et al.
Abstract
Host proteins are essential for HIV entry and replication and can be important nonviral therapeutic targets. Large-scale RNA interference (RNAi)-based screens have identified nearly a thousand candidate host factors, but there is little agreement among studies and few factors have been validated. Here we demonstrate that a genome-wide CRISPR-based screen identifies host factors in a physiologically relevant cell system. We identify five factors, including the HIV co-receptors CD4 and CCR5, that are required for HIV infection yet are dispensable for cellular proliferation and viability. Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 2 (TPST2) and solute carrier family 35 member B2 (SLC35B2) function in a common pathway to sulfate CCR5 on extracellular tyrosine residues, facilitating CCR5 recognition by the HIV envelope. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM) mediates cell aggregation, which is required for cell-to-cell HIV transmission. We validated these pathways in primary human CD4(+) T cells through Cas9-mediated knockout and antibody blockade. Our findings indicate that HIV infection and replication rely on a limited set of host-dispensable genes and suggest that these pathways can be studied for therapeutic intervention.
View All Publications

 网站首页
网站首页