概要
The RosetteSep™ Human CD8+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail is designed to isolate CD8+ T cells from whole blood by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-CD8+ T cells and glycophorin A on red blood cells (RBCs). When centrifuged over a buoyant density medium such as RosetteSep™ DM-L (Catalog #15705) or Lymphoprep™ (Catalog #07801), the unwanted cells pellet along with the RBCs. The purified CD8+ T cells are present as a highly enriched population at the interface between the plasma and the buoyant density medium.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human CD8+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail | 15023, 15063 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human CD8+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail | 15023, 15063 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
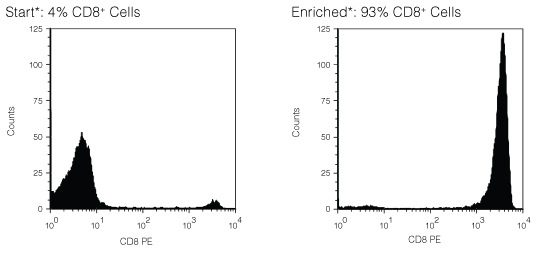
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results Using RosetteSep™ Human CD8+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail
Starting with fresh peripheral blood the CD8+ cell content of the enriched fraction typically ranges from 81% - 95%. *Note: Red blood cells were removed by lysis prior to flow cytometry.
Publications (20)
Nature biomedical engineering 2020 jul
Classification of T-cell activation via autofluorescence lifetime imaging.
Abstract
Abstract
The function of a T cell depends on its subtype and activation state. Here, we show that imaging of the autofluorescence lifetime signals of quiescent and activated T cells can be used to classify the cells. T cells isolated from human peripheral blood and activated in culture using tetrameric antibodies against the surface ligands CD2, CD3 and CD28 showed specific activation-state-dependent patterns of autofluorescence lifetime. Logistic regression models and random forest models classified T cells according to activation state with 97-99{\%} accuracy, and according to activation state (quiescent or activated) and subtype (CD3+CD8+ or CD3+CD4+) with 97{\%} accuracy. Autofluorescence lifetime imaging can be used to non-destructively determine T-cell function.
Nature medicine 2018 OCT
Translational control of tumor immune escape via the eIF4F-STAT1-PD-L1 axis in melanoma.
Abstract
Abstract
Preventing the immune escape of tumor cells by blocking inhibitory checkpoints, such as the interaction between programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptor, is a powerful anticancer approach. However, many patients do not respond to checkpoint blockade. Tumor PD-L1 expression is a potential efficacy biomarker, but the complex mechanisms underlying its regulation are not completely understood. Here, we show that the eukaryotic translation initiation complex, eIF4F, which binds the 5' cap of mRNAs, regulates the surface expression of interferon-$\gamma$-induced PD-L1 on cancer cells by regulating translation of the mRNA encoding the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) transcription factor. eIF4F complex formation correlates with response to immunotherapy in human melanoma. Pharmacological inhibition of eIF4A, the RNA helicase component of eIF4F, elicits powerful antitumor immune-mediated effects via PD-L1 downregulation. Thus, eIF4A inhibitors, in development as anticancer drugs, may also act as cancer immunotherapies.
Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology 2017 MAY
Response to Treatment with TNFα Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated with High Levels of GM-CSF and GM-CSF(+) T Lymphocytes.
Abstract
Abstract
Biologic TNFα inhibitors are a mainstay treatment option for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) refractory to other treatment options. However, many patients either do not respond or relapse after initially responding to these agents. This study was carried out to identify biomarkers that can distinguish responder from non-responder patients before the initiation of treatment. The level of cytokines in plasma and those produced by ex vivo T cells, B cells and monocytes in 97 RA patients treated with biologic TNFα inhibitors was measured before treatment and after 1 and 3 months of treatment by multiplex analyses. The frequency of T cell subsets and intracellular cytokines were determined by flow cytometry. The results reveal that pre-treatment, T cells from patients who went on to respond to treatment with biologic anti-TNFα agents produced significantly more GM-CSF than non-responder patients. Furthermore, immune cells from responder patients produced higher levels of IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6. Cytokine profiling in the blood of patients confirmed the association between high levels of GM-CSF and responsiveness to biologic anti-TNFα agents. Thus, high blood levels of GM-CSF pre-treatment had a positive predictive value of 87.5% (61.6 to 98.5% at 95% CI) in treated RA patients. The study also shows that cells from most anti-TNFα responder patients in the current cohort produced higher levels of GM-CSF and TNFα pre-treatment than non-responder patients. Findings from the current study and our previous observations that non-responsiveness to anti-TNFα is associated with high IL-17 levels suggest that the disease in responder and non-responder RA patients is likely to be driven/sustained by different inflammatory pathways. The use of biomarker signatures of distinct pro-inflammatory pathways could lead to evidence-based prescription of the most appropriate biological therapies for different RA patients.
Diabetes 2017
Type 1 Interferons Potentiate Human CD8+ T-Cell Cytotoxicity Through a STAT4- and Granzyme B-Dependent Pathway.
Abstract
Abstract
Events defining the progression to human type 1 diabetes (T1D) have remained elusive owing to the complex interaction between genetics, the immune system, and the environment. Type 1 interferons (T1-IFN) are known to be a constituent of the autoinflammatory milieu within the pancreas of patients with T1D. However, the capacity of IFNα/β to modulate human activated autoreactive CD8+ T-cell (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) responses within the islets of patients with T1D has not been investigated. Here, we engineer human β-cell-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and demonstrate that T1-IFN augments cytotoxicity by inducing rapid phosphorylation of STAT4, resulting in direct binding at the granzyme B promoter within 2 h of exposure. The current findings provide novel insights concerning the regulation of effector function by T1-IFN in human antigen-experienced CD8+ T cells and provide a mechanism by which the presence of T1-IFN potentiates diabetogenicity within the autoimmune islet.
Cell 2016 SEP
Engineering T Cells with Customized Therapeutic Response Programs Using Synthetic Notch Receptors
Abstract
Abstract
Redirecting T cells to attack cancer using engineered chimeric receptors provides powerful new therapeutic capabilities. However, the effectiveness of therapeutic T cells is constrained by the endogenous T cell response: certain facets of natural response programs can be toxic, whereas other responses, such as the ability to overcome tumor immunosuppression, are absent. Thus, the efficacy and safety of therapeutic cells could be improved if we could custom sculpt immune cell responses. Synthetic Notch (synNotch) receptors induce transcriptional activation in response to recognition of user-specified antigens. We show that synNotch receptors can be used to sculpt custom response programs in primary T cells: they can drive a la carte cytokine secretion profiles, biased T cell differentiation, and local delivery of non-native therapeutic payloads, such as antibodies, in response to antigen. SynNotch T cells can thus be used as a general platform to recognize and remodel local microenvironments associated with diverse diseases.
Cell 2016 FEB
Precision Tumor Recognition by T Cells With Combinatorial Antigen-Sensing Circuits.
Abstract
Abstract
T cells can be re-directed to kill cancer cells using chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) or T cell receptors (TCRs). This approach, however, is constrained by the rarity of tumor-specific single antigens. Targeting antigens also found on bystander tissues can cause life-threatening adverse effects. A powerful way to enhance ON-target activity of therapeutic T cells is to engineer them to require combinatorial antigens. Here, we engineer a combinatorially activated T cell circuit in which a synthetic Notch receptor for one antigen induces the expression of a CAR for a second antigen. These dual-receptor AND-gate T cells are only armed and activated in the presence of dual antigen tumor cells. These T cells show precise therapeutic discrimination in vivo-sparing single antigen bystander" tumors while efficiently clearing combinatorial antigen "disease" tumors. This type of precision dual-receptor circuit opens the door to immune recognition of a wider range of tumors. VIDEO ABSTRACT."

 网站首页
网站首页