概要
The RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Cocktail is designed to enrich lymphoid (CD3+) cells from whole blood by negative selection for lineage-specific chimerism analysis. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing CD16, CD19, CD20, CD36, CD56 and glycophorin A on red blood cells (RBCs). When centrifuged over a buoyant density medium such as RosetteSep™ DM-L (Catalog #15705) the unwanted cells pellet along with the RBCs. The purified lymphoid cells are present as a highly enriched population at the interface between the plasma and the buoyant density medium. The desired cells are immediately ready for chimerism analysis. This kit carries the CE mark and is available as a Class I in vitro diagnostic device in the European Union and Australia. To learn more about the regulatory status of this product in your specific region, contact info@stemcell.com.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet 1 | RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Kit | 15271HLA | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet 2 | RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Kit | 15271HLA | All | MULTI |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Kit | 15271HLA | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Kit | 15271HLA | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
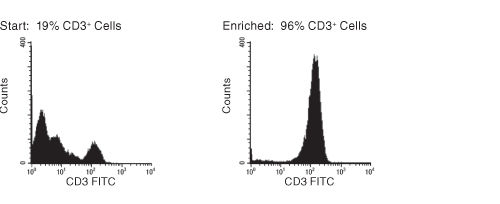
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results with RosetteSep™ HLA Lymphoid Cell Enrichment Kit
Publications (2)
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2005 FEB
Dendritic cells induce MUC1 expression and polarization on human T cells by an IL-7-dependent mechanism.
Abstract
Abstract
The MUC1 transmembrane mucin is expressed on the surface of activated human T cells; however, the physiologic signals responsible for the regulation of MUC1 in T cells are not known. The present studies demonstrate that IL-7, but not IL-2 or IL-4, markedly induces MUC1 expression on CD3+ T cells. MUC1 was also up-regulated by IL-15, but to a lesser extent than that found with IL-7. The results show that IL-7 up-regulates MUC1 on CD4+, CD8+, CD25+, CD69+, naive CD45RA+, and memory CD45RO+ T cells. In concert with induction of MUC1 expression by IL-7, activated dendritic cells (DC) that produce IL-7 up-regulate MUC1 on allogeneic CD3+ T cells. DC also induce MUC1 expression on autologous CD3+ T cells in the presence of recall Ag. Moreover, DC-induced MUC1 expression on T cells is blocked by a neutralizing anti-IL-7 Ab. The results also demonstrate that DC induce polarization of MUC1 on T cells at sites opposing the DC-T cell synapse. These findings indicate that DC-mediated activation of Ag-specific T cells is associated with induction and polarization of MUC1 expression by an IL-7-dependent mechanism.
Blood 2003 NOV
Rapid induction of complete donor chimerism by the use of a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen composed of fludarabine and melphalan in allogeneic stem cell transplantation for metastatic solid tumors.
Abstract
Abstract
We evaluated the feasibility and efficacy of a reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimen of fludarabine and melphalan to achieve rapid complete donor chimerism after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) in patients with metastatic solid tumors. Between January 1999 and January 2003, 8 patients with metastatic breast cancer (BC) and 15 with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) underwent allogeneic SCT after an RIC regimen of 5 days of fludarabine and 2 days of melphalan. Filgrastim-mobilized stem cells from HLA-identical related or unrelated donors were infused. Prophylaxis for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) consisted of tacrolimus and methotrexate. All 22 evaluable patients had 100% donor chimerism at day 30 and at all measurement times thereafter. One patient died 19 days after SCT. Nine patients (39%) had grades II to IV acute GVHD and 10 patients (43%) had chronic GVHD. Five patients (22%) died of nonrelapse treatment-related complications. Treatment-related disease response was seen in 10 patients (45%), with 3 complete responses, 2 partial responses, and 5 minor responses. Fludarabine-melphalan is a feasible and effective RIC regimen for allogeneic SCT in metastatic BC and RCC. It induces rapid complete donor chimerism without the need for donor lymphocyte infusion. Tumor regression associated with GVHD is consistent with graft-versus-tumor effect.

 网站首页
网站首页