概要
This kit is compatible for use with cells from disease models where the malignant cells (B-CLL) express CD43 or CD11b. For isolation of conventional B cells only, we recommend using the EasySep™ Mouse B Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19854).
Click here to learn about our next-generation EasySep™ mouse cell isolation kits, featuring RapidSphere™ technology.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Kit | 19844RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
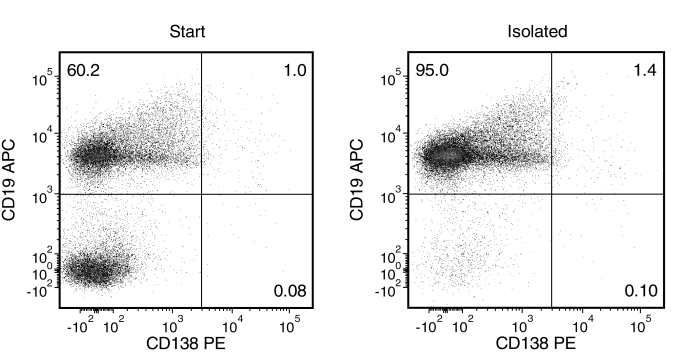
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Profile of a Non-Immunized C57BL/6 Mouse
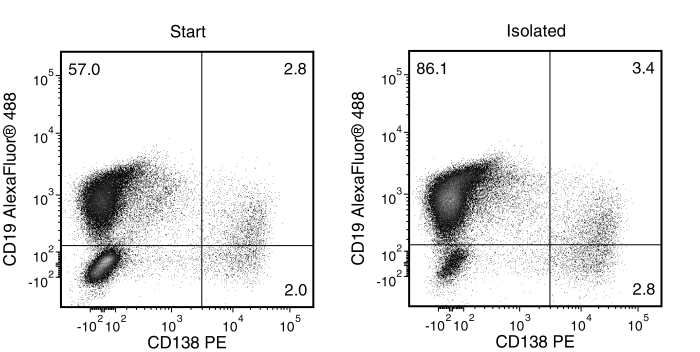
Figure 2. Typical EasySep™ Mouse Pan-B Cell Isolation Profile of an Immunized C57BL/6 Mouse
Starting with mouse splenocytes, the pan-B cell content (CD19+, CD19+CD138+ and CD138+) of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 91 - 98%.

 网站首页
网站首页