概要
The EasySep™ Mouse Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit is designed to isolate mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells from mouse compact bone by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with biotinylated antibodies that are directed against non-mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells (CD45, TER119). Labeled cells are then recognized by Tetrameric Antibody Complexes that are directed against biotin and dextran. These cells are bound to magnetic particles and separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit | 19771 | 18L96978 or higher | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit | 19771 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit | 19771 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
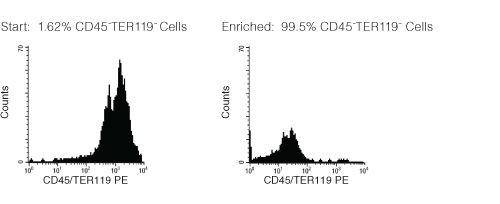
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results with EasySep™ Mouse Mesenchymal Progenitor CellEnrichment Kit
Starting with compact bone, the CD45-TER119- cell content of the enriched cells typically ranges from 50 - 99%. CFU-F enrichment: 50 - 200 fold.
Publications (2)
Biomaterials 2014 MAR
The effect of mesenchymal stem cell sheets on structural allograft healing of critical sized femoral defects in mice.
Abstract
Abstract
Structural bone allografts are widely used in the clinic to treat critical sized bone defects, despite lacking the osteoinductive characteristics of live autografts. To address this, we generated revitalized structural allografts wrapped with mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell (MSC) sheets, which were produced by expanding primary syngenic bone marrow derived cells on temperature-responsive plates, as a tissue-engineered periosteum. In vitro assays demonstrated maintenance of the MSC phenotype in the sheets, suggesting that short-term culturing of MSC sheets is not detrimental. To test their efficacy in vivo, allografts wrapped with MSC sheets were transplanted into 4-mm murine femoral defects and compared to allografts with direct seeding of MSCs and allografts without cells. Evaluations consisted of X-ray plain radiography, 3D microCT, histology, and biomechanical testing at 4- and 6-weeks post-surgery. Our findings demonstrate that MSC sheets induce prolonged cartilage formation at the graft-host junction and enhanced bone callus formation, as well as graft-host osteointegration. Moreover, a large periosteal callus was observed spanning the allografts with MSC sheets, which partially mimics live autograft healing. Finally, biomechanical testing showed a significant increase in the structural and functional properties of MSC sheet grafted femurs. Taken together, MSC sheets exhibit enhanced osteogenicity during critical sized bone defect repair, demonstrating the feasibility of this tissue engineering solution for massive allograft healing.
Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology 2010 APR
Delayed enrichment of mesenchymal cells promotes cardiac lineage and calcium transient development.
Abstract
Abstract
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) can be induced to differentiate into myogenic cells. Despite their potential, previous studies have not been successful in producing a high percentage of cardiac-like cells with a muscle phenotype. We hypothesized that cardiac lineage development in BM-MSC is related to cell passage, culture milieu, and enrichment for specific cell subtypes before and during differentiation. Our study demonstrated that Lin(-) BM-MSC at an intermediate passage (IP; P8-P12) expressed cardiac troponin T (cTnT) after 21 days in culture. Cardiac TnT expression was similar whether IP cells were differentiated in media containing 5-azacytidine+2% FBS (AZA; 14%) or 2% FBS alone (LS; 12%) and both were significantly higher than AZA+5% FBS. This expression was potentiated by first enriching for CD117/Sca-1 cells followed by differentiation (AZA, 39% and LS, 28%). A second sequential enrichment for the dihydropyridine receptor subunit alpha2delta1 (DHPR-alpha2) resulted in cardiac TnT expressed in 54% of cultured cells compared to 28% of cells after CD117/Sca-1(+) enrichment. Cells enriched for CD117/Sca-1 and subjected to differentiation displayed spontaneous intracellular Ca(2+) transients with an increase in transient frequency and a 60% decrease in the transient duration amplitude between days 14 and 29. In conclusion, IP CD117/Sca-1(+) murine BM-MSCs display robust cardiac muscle lineage development that can be induced independent of AZA but is diminished under higher serum concentrations. Furthermore, temporal changes in calcium kinetics commensurate with increased cTnT expression suggest progressive maturation of a cardiac muscle lineage. Enrichment with CD117/Sca-1 to establish lineage commitment followed by DHPR-alpha2 in lineage developing cells may enhance the therapeutic potential of these cells for transplantation.

 网站首页
网站首页



