概要
The EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II is designed to isolate CD90.2+ (Thy1.2+) cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by positive selection. Desired cells are targeted with antibody complexes recognizing CD90.2 and dextran-coated magnetic particles. Labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Cells of interest remain in the tube while unwanted cells are poured off.
This product replaces the EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18751) for even faster cell isolations and does not result in the labeling of isolated cells with PE.
This product replaces the EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18751) for even faster cell isolations and does not result in the labeling of isolated cells with PE.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Mouse CD90.2 Positive Selection Kit II | 18951RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
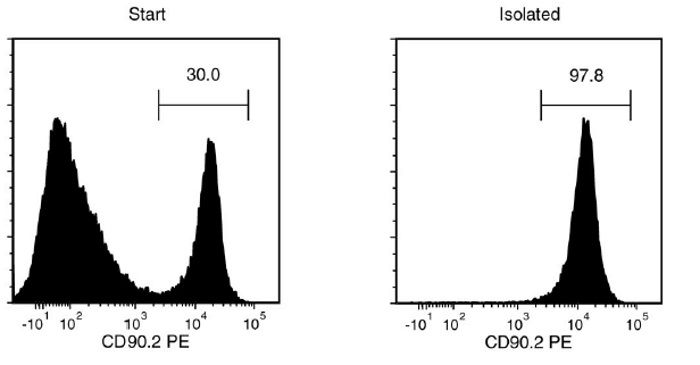
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ CD90.2 Positive Selection II Profile
Starting with mouse splenocytes, the CD90.2+ cell content of the isolated fraction is typically 95.8 ± 1.5% (mean ± SD using the purple EasySep™ Magnet).
Publications (1)
Frontiers in immunology 2019
Macrophage Coordination of the Interferon Lambda Immune Response.
Abstract
Abstract
Lambda interferons (IFN-$\lambda$s) are a major component of the innate immune defense to viruses, bacteria, and fungi. In human liver, IFN-$\lambda$ not only drives antiviral responses, but also promotes inflammation and fibrosis in viral and non-viral diseases. Here we demonstrate that macrophages are primary responders to IFN-$\lambda$, uniquely positioned to bridge the gap between IFN-$\lambda$ producing cells and lymphocyte populations that are not intrinsically responsive to IFN-$\lambda$. While CD14+ monocytes do not express the IFN-$\lambda$ receptor, IFNLR1, sensitivity is quickly gained upon differentiation to macrophages in vitro. IFN-$\lambda$ stimulates macrophage cytotoxicity and phagocytosis as well as the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and interferon stimulated genes that mediate immune cell chemotaxis and effector functions. In particular, IFN-$\lambda$ induced CCR5 and CXCR3 chemokines, stimulating T and NK cell migration, as well as subsequent NK cell cytotoxicity. Using immunofluorescence and cell sorting techniques, we confirmed that human liver macrophages expressing CD14 and CD68 are highly responsive to IFN-$\lambda$ ex vivo. Together, these data highlight a novel role for macrophages in shaping IFN-$\lambda$ dependent immune responses both directly through pro-inflammatory activity and indirectly by recruiting and activating IFN-$\lambda$ unresponsive lymphocytes.

 网站首页
网站首页