概要
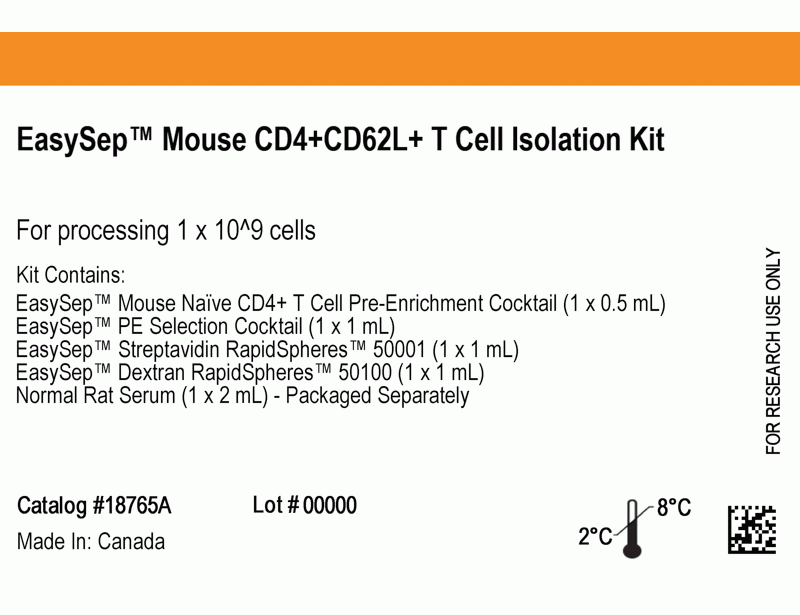
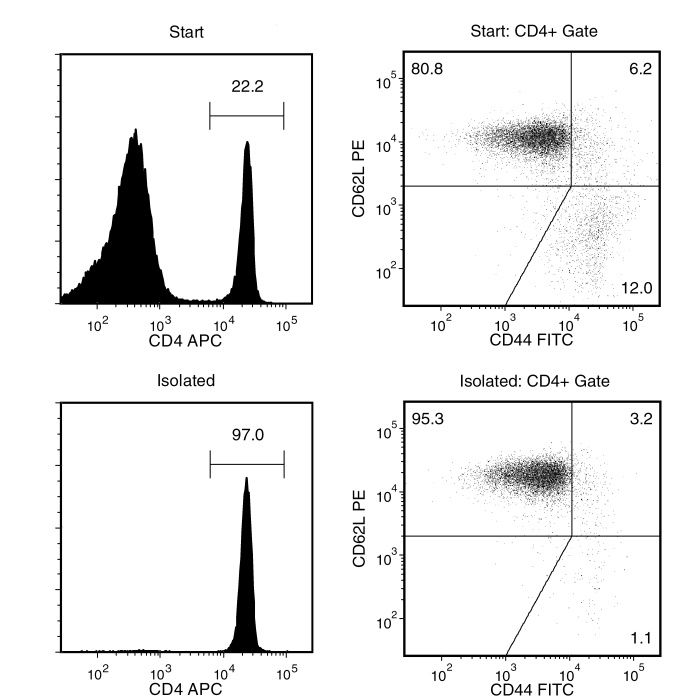
Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by using a simple, two-step method. First, naive CD4+ T cells are pre-enriched by negative selection using the EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Pre-Enrichment Cocktail containing biotinylated antibodies directed against non-naïve CD4+ T cells (CD8, CD11b, CD11c, CD19, CD24, CD25, CD45R, CD49b, TCRγ/δ, TER119). Then CD4+CD62L+ cells, pre-labeled with CD62L PE, are selected using the EasySep™ PE Selection Cocktail. The desired cells are labeled with antibodies and magnetic particles. The cells are separated without columns using an EasySep™ magnet.
For the isolation of mouse naïve CD4+ T cells in as little as 15 minutes by negative selection, we recommend using the EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (19765).
数据及文献
Publications (2)
Cell reports 2020 may
Targeting Lymph Node Niches Enhances Type 1 Immune Responses to Immunization.
J. Lian et al.
Abstract
Generating robust CD4+ T-helper cell type 1 (Th1) responses is essential for protective vaccine-induced type 1 immunity. Here, we examine whether immunization formulation associated with enhanced vaccine efficacy promotes antigen targeting and cell recruitment into lymph node (LN) niches associated with optimal type 1 responses. Immunization with antigen and Toll-like receptor agonist emulsified in oil leads to an increased differentiation of IFN$\gamma$/TNF-$\alpha$+ polyfunctional Th1 cells compared to an identical immunization in saline. Oil immunization results in a rapid delivery and persistence of antigen in interfollicular regions (IFRs) of the LN, whereas without oil, antigen is distributed in the medullary region. Following oil immunization, CXCL10-producing inflammatory monocytes accumulate in the IFR, which mobilizes antigen-specific CD4+ T cells into this niche. In this microenvironment, CD4+ T cells are advantageously positioned to encounter arriving IL-12-producing inflammatory dendritic cells (DCs). These data suggest that formulations delivering antigen to the LN IFR create an inflammatory niche that can improve vaccine efficacy.
Journal of autoimmunity 2019 may
NF-kappaB-driven miR-34a impairs Treg/Th17 balance via targeting Foxp3.
M. Xie et al.
Abstract
The subset of regulatory T (Treg) cells, with its specific transcription Foxp3, is a unique cell type for the maintenance of immune homeostasis by controlling effector T (Teff) cell responses. Although it is common that a defect in Treg cells with Treg/Teff disorder causes autoimmune diseases; however, the precise mechanisms are not thoroughly revealed. Here, we report that miR-34a could attenuate human and murine Foxp3 gene expression via targeting their 3' untranslated regions (3' UTR). The human miR-34a, increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and CD4+ T cells from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, displayed a positive correlation with some serum markers of inflammation including rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-streptolysin antibody (ASO), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) as well as Th17 signature gene RORgammat, but inversely correlated with the mRNA expression levels of FOXP3. In addition, murine miR-34a levels were downregulated in TGF-beta-induced Treg cells but upregulated in Th17 cells induced in vitro compared to activated CD4+ T cells. It has also been demonstrated that elevated miR-34a disrupting Treg/Th17 balance in vivo contributed to the progress of pathogenesis of collagen induced arthritis (CIA) mice. Furthermore, IL-6 and TNF-alpha were responsible for the upregulation of miR-34a and downregulation of Foxp3, which was reverted by the addition of NF-kappaB/p65 inhibitor BAY11-7082, thus indicating that NF-kappaB/p65 inhibited Foxp3 expression in an miR-34a-dependent manner. Finally, IL-6 or TNF-alpha-activated p65 could bind to the miR-34a promotor and enhance its activity, resulting in upregulation of its transcription. Taken together, we show that NF-kappaB activated by inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha, ameliorates Foxp3 levels via regulating miR-34a expression, which provides a new mechanistic and therapeutic insight into the ongoing of autoimmune diseases.
View All Publications

 网站首页
网站首页