概要
MegaCult™-C Staining Kit for CFU-Mk contains all the reagents needed to stain fixed and dehydrated CFU-Mk colonies cultured in MegaCult™-C collagen-based medium. Megakaryocytes and platelets expressing the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa are stained with anti-human CD41 antibody and an alkaline phosphatase detection system. The kit is also suitable for detection of bipotential erythroid-megakaryocyte progenitor cells (BFU-E/Mk).
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | MegaCult™-C Staining Kit for CFU-Mk | 04962 | All | English |
| Manual | MegaCult™-C Staining Kit for CFU-Mk | 04962 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Staining Kit for CFU-Mk | 04962 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Primary Antibody | 04803 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Control Antibody | 04804 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Human Serum | 04807 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Alkaline Phosphatase Substrate Tablets | 04809 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Avidin-Alkaline Phosphatase Conjugate | 04905 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Biotin-Conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse IgG | 04906 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C Evans Blue Stain | 04913 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MegaCult™-C 10% BSA | 04915 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
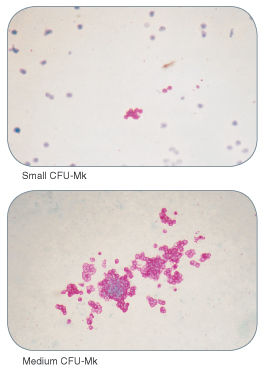
Figure 1. Examples of Colonies Derived from Human Megakaryocyte Progenitors
Publications (5)
The hematology journal : the official journal of the European Haematology Association / EHA 2001 JAN
Comparison of four serum-free, cytokine-free media for analysis of endogenous erythroid colony growth in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia.
Abstract
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: The assay of endogenous erythroid colony formation (EEC), a characteristic of polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, is not standardized. In this multicentric study, we tested four semisolid, serum-free, cytokine-free media based on either methylcellulose (M1, M2) or collagen (C1, C2) commercialized for the EEC assay. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMC) from 73 individuals (62 patients with either polycythemia vera (26), essential thrombocythemia (19), secondary polyglobuly (17) or chronic myeloid leukemia (2) and 11 healthy donors) were grown in parallel in the four media without, or with 0.01 U/ml erythropoietin (EPo). RESULTS: In all four media EEC formation was specific, as it was not observed in cultures of patients with secondary polyglobuly or chronic myeloid leukemia, nor of healthy donors. Analysis of fresh or MGG-stained collagen gel cultures allowed detection of EEC formation significantly more frequently than methylcellulose-based media; addition of 0.01 U/ml of EPo had little or no effect on EEC formation. Collagen-based medium C1 gave better results than the other media tested: the 'C1' EEC assay was positive for 68.2% of polycythemia vera cultures with significantly higher median EEC numbers (6.5/10(5) BMMC for patients with one major criteria of polycythemia vera and 19 and 21/10(5) BMMC for patients with two or three major criteria, respectively). Medium C1 was also better for essential thrombocythemia cultures with 47.4% of positive results but with a low median EEC number (6.7/10(5) BMMC). When associated with the ELISA dosage of serum EPo, the 'C1' EEC assay allowed confirmation or elimination of the diagnosis of polycythemia vera for 91% (20/22) of polyglobulic patients. CONCLUSION: We propose that serum-free collagen-based culture systems be considered to standardize the EEC assay, now part of the new criteria of polycythemia vera.
Journal of hematotherapy & stem cell research 1999 DEC
Endogenous erythroid and megakaryocytic colony formation in serum-free, cytokine-free collagen gels.
Abstract
Abstract
We studied the suitability of collagen-based semisolid medium for assay of endogenous erythroid colony formation performed in myeloproliferative disorders. Bone marrow (BM) mononuclear cells (MNC) from 103 patients suspected of having polycythemia vera (PV, 76 patients) or essential thrombocythemia (ET, 27 patients) were grown in collagen-based, serum-free, cytokine-free semisolid medium. Colony analysis at day 8 or 10 showed that this collagen assay is specific, as endogenous growth of erythroid colonies was never observed in cultures of 16 healthy donors and 6 chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients. Endogenous erythroid colony formation was observed in 53.3% of patients suspected of PV, with only 15.4% of positive cultures for patients with 1 minor PV criterion and 72% (p = 0.009) of positive cultures for patients with textgreater or =2 minor or 1 major PV criterion. Similarly, endogenous growth of erythroid colonies was found in 44.4% of patients suspected of ET, with 31.6% of positive cultures for patients with 1 ET criterion versus 75% for patients with textgreater or =2 ET criteria. In addition, we found that in collagen gels, tests of erythropoietin (EPO) hypersensitivity in the presence of 0.01 or 0.05 U/ml of EPO and tests of endogenous colony-forming units-megakaryocyte (CFU-MK) formation cannot be used to detect PV or ET, as these tests were positive for, respectively, 21.4% and 50% of healthy donors and 83% and 50% of CML patients. A retrospective analysis suggests that collagen assays are more sensitive than methylcellulose assays to assess endogenous growth of erythroid colonies. In summary, serum-free collagen-based colony assays are simple and reliable assays of endogenous growth of erythroid colonies in myeloproliferative diseases. They also appear to be more sensitive than methylcellulose-based assays.
British journal of haematology 1997 MAR
Quantitation and characterization of human megakaryocyte colony-forming cells using a standardized serum-free agarose assay.
Abstract
Abstract
Human progenitors of the megakaryocyte (Mk) lineage were detected by their ability to generate colonies-containing from 3 to textgreater 100 Mk, detectable as glycoprotein IIb/IIIa+ cells in APAAP-stained whole mount agarose cultures. Optimal growth conditions were achieved through the use of a defined serum substitute and a suitable cocktail of recombinant cytokines. Under these culture conditions, the smallest Mk-containing colonies (CFC-Mk) were detectable within a week followed by colonies containing larger numbers of Mk over the ensuing 2 weeks. The total number of CFC-Mk at 18-21 d was linearly related to the number of cells plated. Variation in the cytokines added showed that thrombopoietin (TPO) or IL-3 alone would support the formation of large numbers of CFC-Mk. However, optimal yields of colonies containing cells of both Mk and non-Mk lineages required the addition of other growth factors, of which a combination of IL-3, IL-6, GM-CSF and Steel factor (SF) +/- TPO was the best of those tested. The further addition of erythropoietin to this combination reduced the number of large pure' Mk colonies seen and in their place a corresponding number of mixed erythroid-Mk colonies became detectable. Flt3-ligand alone was unable to support the growth of CFC-Mk nor did it enhance their growth when combined with other factors. Plating of FACS-sorted sub-populations of CD34+ marrow cells in both serum-free agarose and methylcellulose assays demonstrated that most CFC-Mk are generated from CD34+ cells that are CD45RA- and CD71+�
Journal of hematotherapy 1995 AUG
Collagen matrix: an attractive alternative to agar and methylcellulose for the culture of hematopoietic progenitors in autologous transplantation products.
Abstract
Abstract
Autografts using untreated or in vitro manipulated bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cells represent promising approaches to the treatment of malignant diseases. In this work, the collagen gel culture technique was compared with agar and methylcellulose for its capacity to permit the growth of human granulomonocytic (day 14 CFU-GM; collagen vs agar or MTC) or erythroblastic (day 7 CFU-E and day 14 BFU-E; collagen versus methylcellulose) colonies in autologous transplantation products. Our results show that the collagen culture system always gave as many or more colonies than the other techniques. It also allowed harvesting of gels onto glass slides and subsequent May-Grünwald-Giemsa, cytochemical or immunocytochemical staining. We suggest that the collagen assay represents an interesting alternative to the widely used agar or methylcellulose systems for the culture of hematopoietic progenitors because of the equal or higher number of colonies detected, the easy phenotypical identification of colonies in stained gels, and the ability to store high-quality documentation. This technique is particularly attractive for use in the quality control of autologous bone marrow transplantation procedures.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 1993 MAR
Serum-free medium allows the optimal growth of human megakaryocyte progenitors compared with human plasma supplemented cultures: role of TGF beta.
Abstract
Abstract
The growth of human megakaryocyte progenitors from human bone marrow (BM) cells was compared using a methylcellulose semisolid assay supplemented either by normal human plasma or by a serum-free medium. Far better growth of megakaryocyte colonies from CD34+ BM cells stimulated by interleukin 3 (IL-3) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) was observed in serum-free medium compared with human plasma supplemented cultures. These results were confirmed in liquid cultures using the same serum-free medium composition. The megakaryocytes were identified by using an immunocytochemical procedure after labeling with an anti-GPIIb-IIIa monoclonal antibody. High percentages (15 to 20%) of megakaryocytes were present in serum-free cultures stimulated by IL-3 alone or combined with IL-6. The absolute number of megakaryocytes in serum-free medium exceeds by 3.3 (IL-3 plus IL-6) to 4.4 (IL-3 alone) times the corresponding number of megakaryocytes observed in human plasma supplemented cultures. The optimal concentration of IL-3 alone was 5 ng/ml, and an optimal synergistic effect of IL-6 (5 ng/ml) was obtained when combined with a suboptimal dose of IL-3 (1 ng/ml). The poor growth of megakaryocyte colonies from CD34+ BM cells in human plasma suggested the presence of an inhibitory factor. When a neutralizing monoclonal antibody against transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) is present in human plasma supplemented cultures of CD34+ BM cells, the number of megakaryocyte colonies is increased to the level observed in corresponding serum-free cultures. The high efficiency of this serum-free medium to promote the growth of human megakaryocytes will be useful to study the effects of regulators and platelet agonists acting on human megakaryocytes, without interference from factors in the serum.

 网站首页
网站首页