概要
To enhance cell quality attributes, particularly during restricted feeds, critical medium components have been stabilized, including fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2; also known as basic FGF [bFGF]). As a result, TeSR™-AOF allows for compatibility with both daily and restricted feeding schedules while maintaining cell quality and equivalent performance.
TeSR™-AOF is compatible with a variety of culture matrices, including Corning® Matrigel® hESC-Qualified Matrix (Corning Catalog #354277), Vitronectin XF™ (Catalog #07180), Biolaminin 521 MX (BioLamina Catalog #MX521), and Biolaminin 521 CTG (BioLamina Catalog #CT521).
No materials of animal or human origin are used in the manufacture of this medium or its components, to at least the secondary level of manufacturing. TeSR™-AOF is animal component-free to the secondary level. Each lot of TeSR™-AOF 20X Supplement that is used to prepare complete TeSR™-AOF medium is performance-tested in a culture assay using human pluripotent stem cells.
This product is designated a prototype. It has been manufactured using qualified materials in our GMP manufacturing facility but has not completed our full cGMP qualification.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | TeSR™-AOF | 100-0401 | All | English |
| Manual | TeSR™-AOF | 100-0401 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | TeSR™-AOF | 100-0401 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | TeSR™-AOF | 100-0401 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data

Figure 1A. hPSCs Maintained in TeSR™-AOF with Daily and Restricted Feed Schedules Exhibit Comparable Colony Morphology
hPSCs were maintained on Vitronectin XF™ for five passages. Phase-contrast images were taken on day 7 after seeding. For restricted feeds, hPSCs were fed with a double volume (4 mL) of medium on day 2 after passage, followed by two consecutive skipped days of feeds, with a final single-volume feed (2 mL) on day 5, prior to passaging on day 6 or 7.
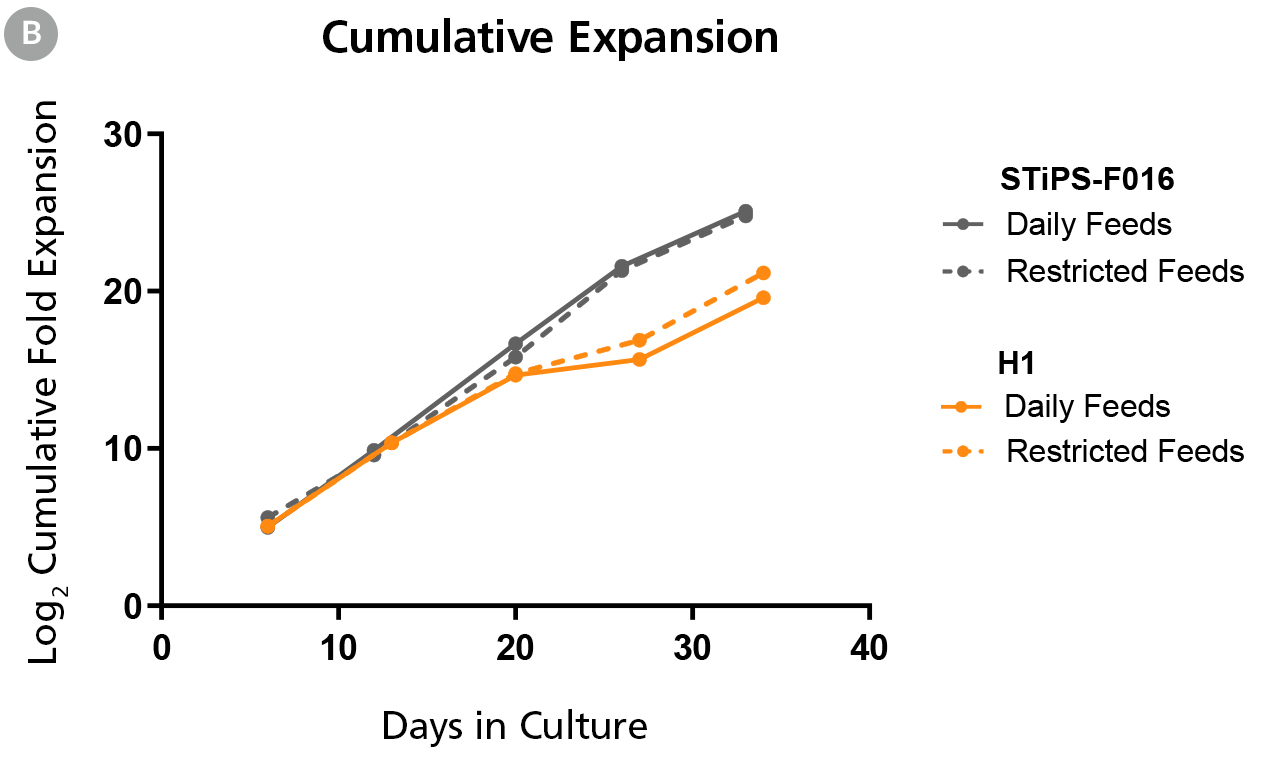
Figure 1B. hPSCs Maintained in TeSR™-AOF with Daily and Restricted Feed Schedules have Comparable Expansion Rates
hPSCs were maintained on Vitronectin XF™ for five passages. At the end of each passage cell counts were obtained using the Nucleocounter®️ NC-200 ChemoMetec automated cell counter to count DAPI-stained nuclei. The log2 transformed cumulative fold expansion was plotted against time in culture (days).
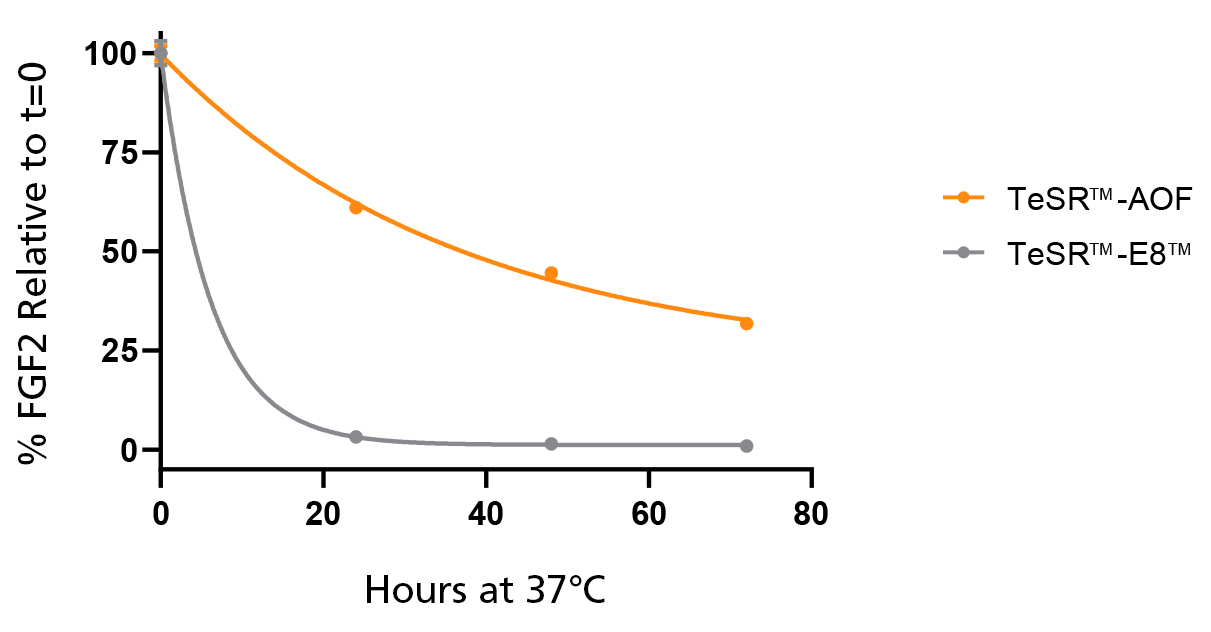
Figure 2. Native bFGF Levels are Stabilized at 37°C in TeSR™-AOF
TeSR™-AOF and TeSR™-E8™ were incubated at 37°C for 24, 48, and 72 hours. FGF2 levels were measured by Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) immunoassay; data was normalized to t = 0 levels for TeSR™-E8™ and TeSR™-AOF, respectively. FGF2 levels in TeSR™-AOF remain at 36.7 ± 5.61% of t = 0 levels at 72 hours when incubated at 37°C. Data representative of n = 3 biological replicates ± SD.
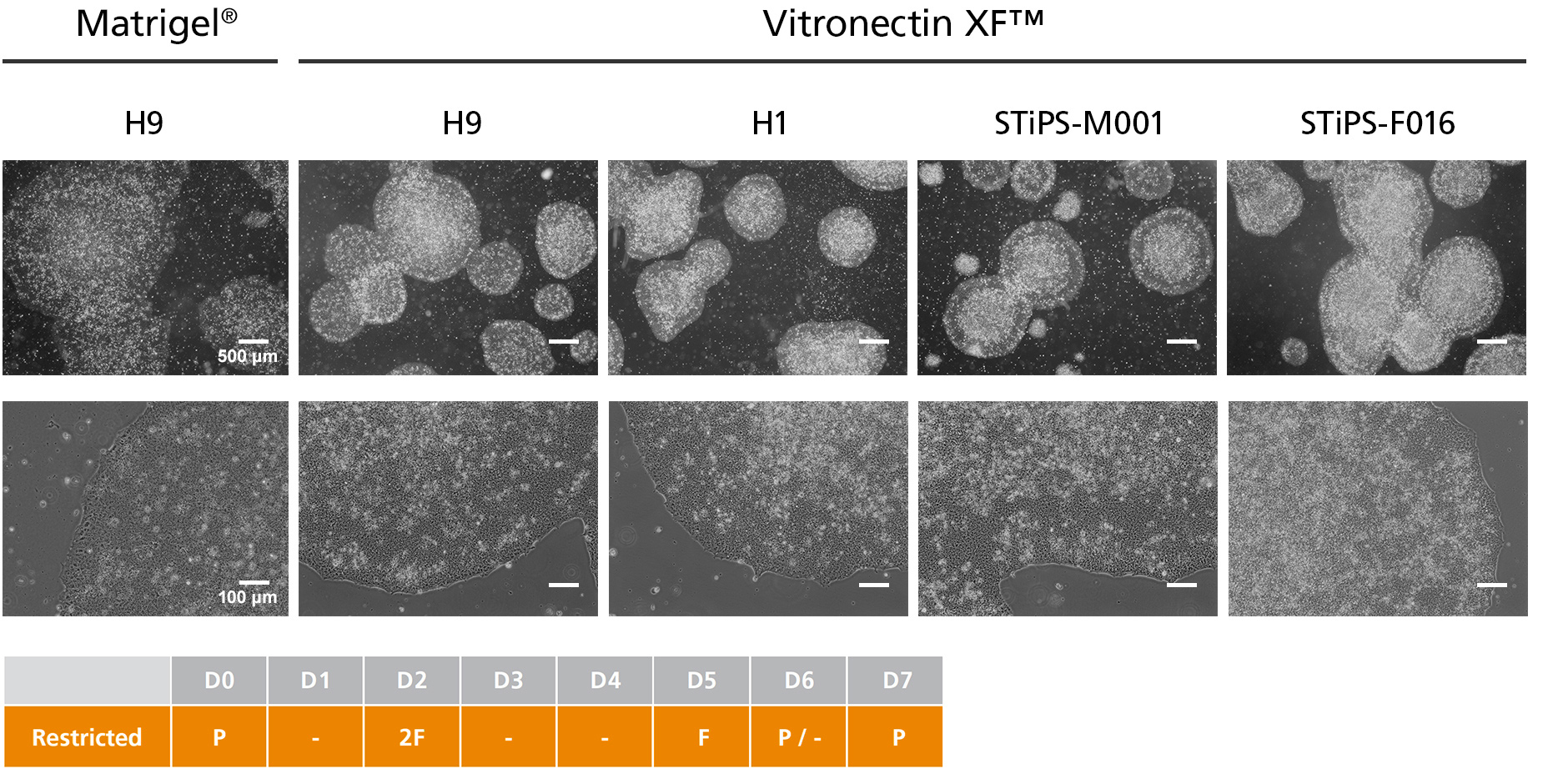
Figure 3. hPSCs Cultured in TeSR™-AOF with Restricted Feeding Maintain Demonstrate Classic hPSC Colony Morphology
hPSCs maintained in TeSR™-AOF were passaged as aggregates with ReLeSR™ passaging reagent every 6-7 days for greater than 10 passages. hPSCs maintained in TeSR™-AOF exhibit hPSC-like morphology, forming densely packed, round colonies with smooth edge morphology. Homogeneous cell morphology characteristic of hPSCs are observed, including large nucleoli and scant cytoplasm.

Figure 4. hPSCs Maintained in TeSR™-AOF Have Improved Attachment and Higher Overall Expansion Compared to Low-Protein Medium
(A) hPSCs cultured in TeSR™-AOF demonstrate a higher plating efficiency compared to hPSCs maintained in low-protein medium (TeSR™-E8™). Plating efficiency is calculated by seeding a known number of aggregates and comparing to the number of established colonies on day 7. (B) hPSCs maintained in TeSR™-AOF exhibit a higher average fold expansion per passage compared to TeSR™-E8™. (C) hPSCs cultured in TeSR™-AOF demonstrate consistent expansion and minimal cell line-to-cell-line variability between ES and iPS cell lines assessed. Cumulative fold expansion was measured from passage 1 to 5. Data represented as mean plating efficiency or fold expansion across 10 passages ± SD. MG = Matrigel®; VN = Vitronectin XF™.
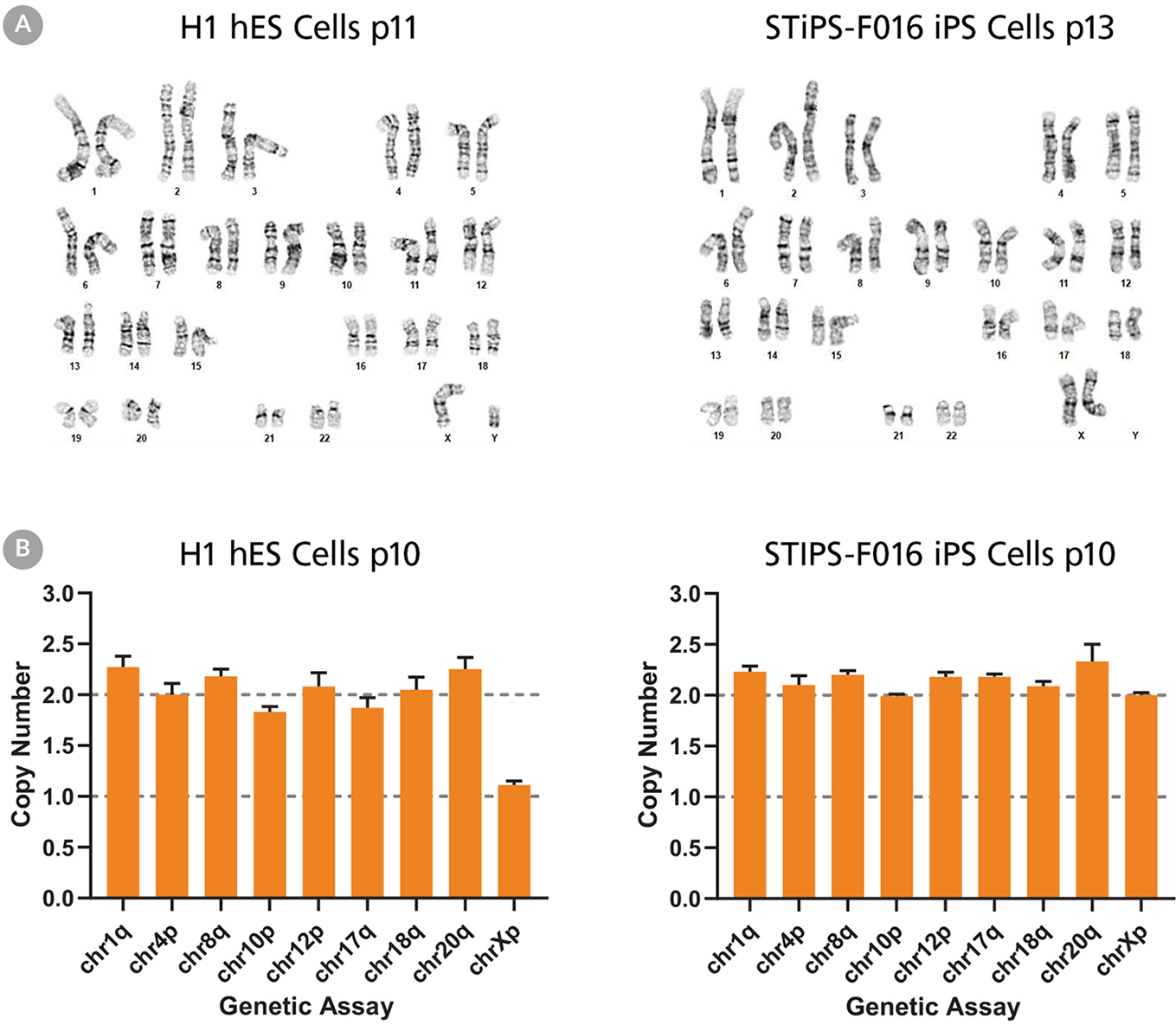
Figure 5. hPSCs Cultured in TeSR™-AOF with Restricted Feeding Maintain a Normal Karyotype
ES (H9 & H1) and iPS (STiPS-M001 & STiPS-F016) cell lines cultured in TeSR™-AOF were screened for chromosomal abnormalities using the hPSC Genetic Analysis Kit and by G-banding at ≥ 10 passages. Representative data are shown for (A) H1 ES and STiPS-F016 hiPS cell cultures at passage 10; no common chromosomal abnormalities were detected using the hPSC Genetic Analysis Kit, and (B) H1 ES cultures; these displayed a normal karyotype by G-banding at passage 11 and 13 respectively.
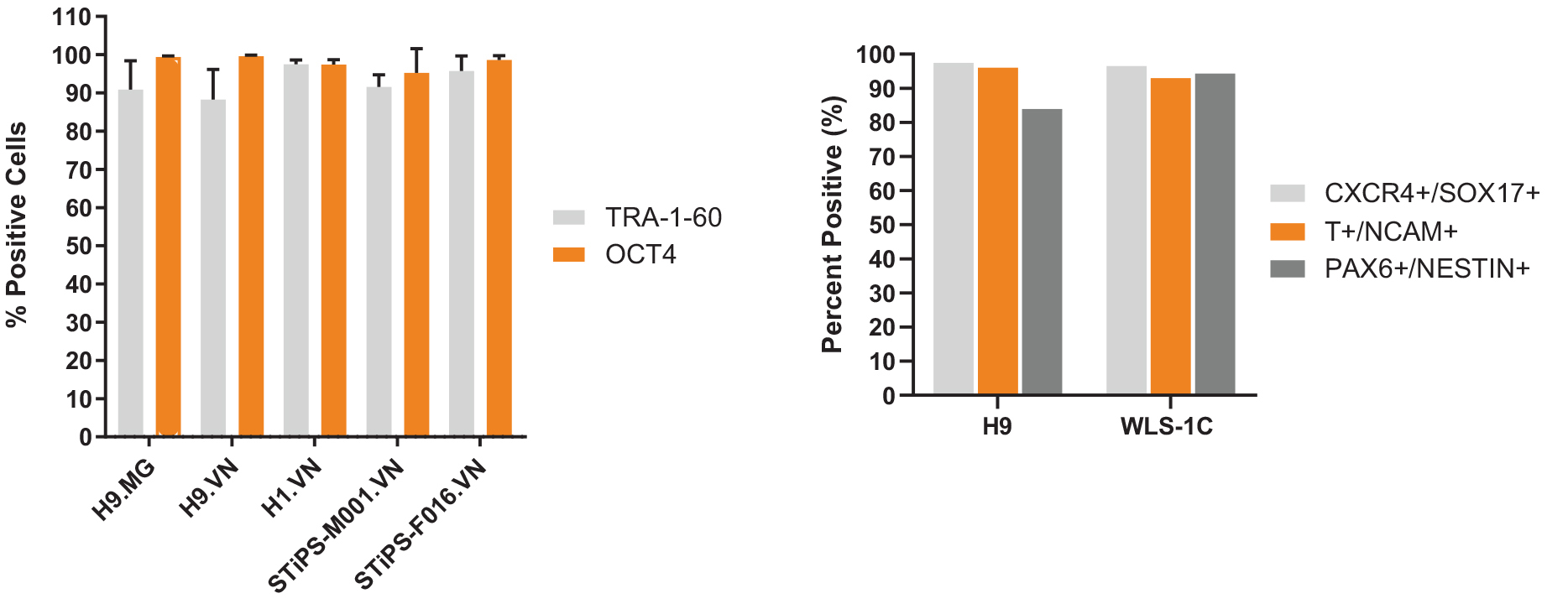
Figure 6. hPSCs Cultured in TeSR™-AOF Express Markers of the Undifferentiated State and Differentiate to the Three Germ Layers
(A) hPSCs maintained in TeSR™-AOF exhibit high levels of TRA-1-60 and OCT4 by flow cytometry at passage 5 and 10. Across n = 5 cell lines, the average TRA-1-60 expression was 92.8 ± 3.77 %, and percent OCT-4 positive cells were 98.1 ± 1.79%. Data shown represent an average of passage 5 and 10 flow results for each cell line. MG = Matrigel®; VN = Vitronectin XF™. (B) Efficient differentiation to the three germ layers was demonstrated in one hES and one hiPS cell line maintained for > 5 passages in TeSR™-AOF. Cultures were processed for flow cytometry and assessed for CXCR4+/SOX17+ cells on day 5 following differentiation using the STEMdiff™ Definitive Endoderm Kit. Cultures were processed for flow cytometry and assessed for Brachyury (T)+/OCT4- cells on day 5 following differentiation in STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium. Cultures were processed for flow cytometry and assessed for PAX6+/Nestin+ cells on day 7 following monolayer differentiation using STEMdiff™ Neural Induction Medium.
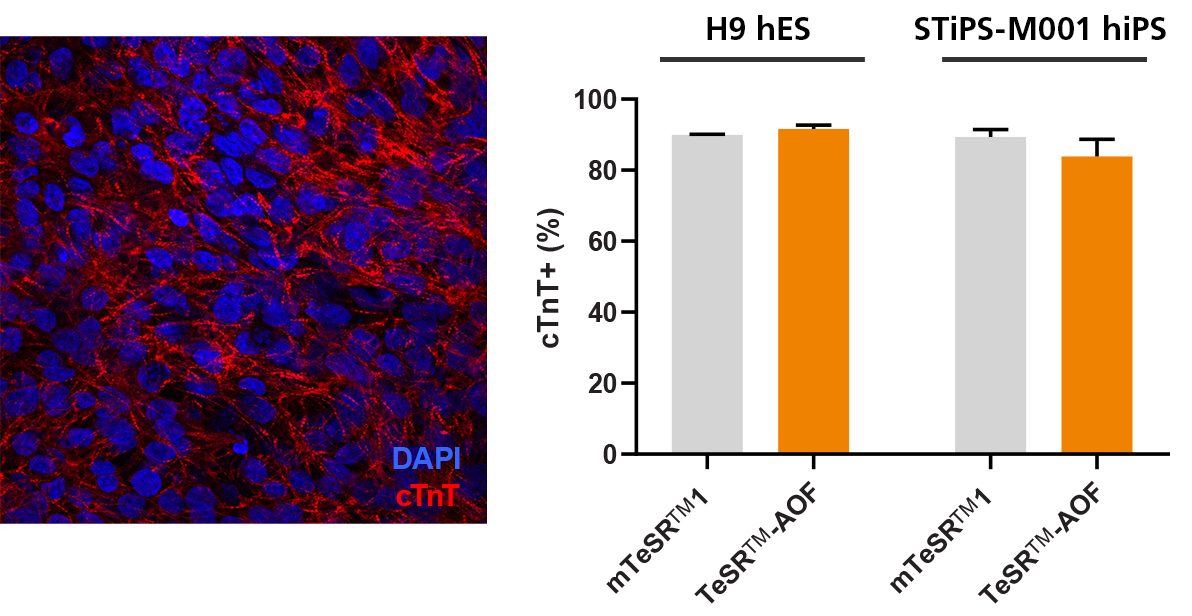
Figure 7. hPSCs Culture in TeSR™-AOF Differentiate to Cardiomyocytes with the STEMdiff™ Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit
Efficient differentiation to cardiomyocytes was demonstrated in 1 hES and 1 hiPS cell line maintained in TeSR™-AOF using the STEMdiff™ Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit. Expression of cardiac troponin T (cTnT) was assessed by immunocytochemistry (ICC) and by flow cytometry.

 网站首页
网站首页