概要
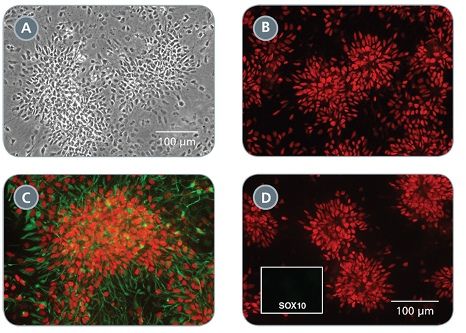
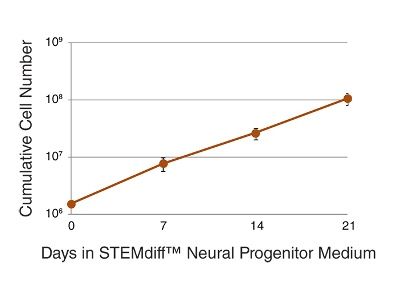
STEMdiff™ Neural Progenitor Medium is a defined and serum-free medium for the expansion of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived from human embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells using STEMdiff™ Neural Induction Medium (Catalog #05835). NPCs cultured in this medium can be expanded 3-5 fold per passage, and cultured for at least 10 passages, with minimal spontaneous neuronal differentiation.
数据及文献
Publications (15)
Viruses 2020 mar
Modelling Lyssavirus Infections in Human Stem Cell-Derived Neural Cultures.
V. Sundaramoorthy et al.
Abstract
Rabies is a zoonotic neurological infection caused by lyssavirus that continues to result in devastating loss of human life. Many aspects of rabies pathogenesis in human neurons are not well understood. Lack of appropriate ex-vivo models for studying rabies infection in human neurons has contributed to this knowledge gap. In this study, we utilize advances in stem cell technology to characterize rabies infection in human stem cell-derived neurons. We show key cellular features of rabies infection in our human neural cultures, including upregulation of inflammatory chemokines, lack of neuronal apoptosis, and axonal transmission of viruses in neuronal networks. In addition, we highlight specific differences in cellular pathogenesis between laboratory-adapted and field strain lyssavirus. This study therefore defines the first stem cell-derived ex-vivo model system to study rabies pathogenesis in human neurons. This new model system demonstrates the potential for enabling an increased understanding of molecular mechanisms in human rabies, which could lead to improved control methods.
Biosensors 2019 apr
A Novel Toolkit for Characterizing the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Engineered Neural Tissues.
M. Robinson et al.
Abstract
We have designed and validated a set of robust and non-toxic protocols for directly evaluating the properties of engineered neural tissue. These protocols characterize the mechanical properties of engineered neural tissues and measure their electrophysical activity. The protocols obtain elastic moduli of very soft fibrin hydrogel scaffolds and voltage readings from motor neuron cultures. Neurons require soft substrates to differentiate and mature, however measuring the elastic moduli of soft substrates remains difficult to accurately measure using standard protocols such as atomic force microscopy or shear rheology. Here we validate a direct method for acquiring elastic modulus of fibrin using a modified Hertz model for thin films. In this method, spherical indenters are positioned on top of the fibrin samples, generating an indentation depth that is then correlated with elastic modulus. Neurons function by transmitting electrical signals to one another and being able to assess the development of electrical signaling serves is an important verification step when engineering neural tissues. We then validated a protocol wherein the electrical activity of motor neural cultures is measured directly by a voltage sensitive dye and a microplate reader without causing damage to the cells. These protocols provide a non-destructive method for characterizing the mechanical and electrical properties of living spinal cord tissues using novel biosensing methods.
Frontiers in genetics 2019
Linc-GALMD1 Regulates Viral Gene Expression in the Chicken.
Y. He et al.
Abstract
A rapidly increasing number of reports on dysregulated long intergenic non-coding RNA (lincRNA) expression across numerous types of cancers indicates that aberrant lincRNA expression may be a major contributor to tumorigenesis. Marek's disease (MD) is a T cell lymphoma of chickens induced by Marek's disease virus (MDV). Although we have investigated the roles of lincRNAs in bursa tissue of MDV-infected chickens in previous studies, the molecular mechanisms of lincRNA functions in T cells remain poorly understood. In the present study, Linc-GALMD1 was identified from CD4+ T cells and MSB1 cells, and its expression was significantly downregulated in MD-resistant line of birds in response to MDV challenge. Furthermore, loss-of-function experiments indicated that linc-GALMD1 significantly affected the expression of 290 genes in trans. Through integrated analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) induced by MDV and linc-GALMD1, we found that IGLL1 gene expression levels had a positive correlation with the degree of MD infection and could potentially serve as an indicator for clinical diagnosis of MD. Moreover, an interaction between MDV and linc-GALMD1 was also observed. Accordingly, chicken embryonic fibroblast cells were inoculated with MDV with and without the linc-GALMD1 knockdown, and the data showed that linc-GALMD1 could repress MDV gene expression during the course of MDV infection. These findings uncovered a role of linc-GALMD1 as a viral gene regulator and suggested a function of linc-GALMD1 contributing to tumor suppression by coordinating expression of MDV genes and tumor-related genes and regulating immune responses to MDV infection.
Stem cell reports 2018 JUL
Disruption of GRIN2B Impairs Differentiation in Human Neurons.
S. Bell et al.
Abstract
Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in GRIN2B, a subunit of the NMDA receptor, cause intellectual disability and language impairment. We developed clonal models of GRIN2B deletion and loss-of-function mutations in a region coding for the glutamate binding domain in human cells and generated neurons from a patient harboring a missense mutation in the same domain. Transcriptome analysis revealed extensive increases in genes associated with cell proliferation and decreases in genes associated with neuron differentiation, a result supported by extensive protein analyses. Using electrophysiology and calcium imaging, we demonstrate that NMDA receptors are present on neural progenitor cells and that human mutations in GRIN2B can impair calcium influx and membrane depolarization even in a presumed undifferentiated cell state, highlighting an important role for non-synaptic NMDA receptors. It may be this function, in part, which underlies the neurological disease observed in patients with GRIN2B mutations.
Neuroscience letters 2017 JAN
Generation of disease-specific autopsy-confirmed iPSCs lines from postmortem isolated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Belle K et al.
Abstract
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie neurodegenerative disorders has been hampered by a lack of readily available model systems that replicate the complexity of the human disease. Recent advances in stem cell technology have facilitated the derivation of patient-specific stem cells from a variety of differentiated cell types. These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are attractive disease models since they can be grown and differentiated to produce large numbers of disease-relevant cell types. However, most iPSC lines are derived in advance of, and without the benefit of, neuropathological confirmation of the donor - the gold standard for many disease classifications and measurement of disease severity. While others have reported the generation of autopsy-confirmed iPSC lines from patient explants, these methods require outgrowth of cadaver tissue, which require additional time and is often only successul 50% of the time. Here we report the rapid generation of autopsy-confirmed iPSC lines from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) drawn postmortem. Since this approach doesn't require the propagation of previously frozen cadaver tissue, iPSC can be rapidly and efficiently produced from patients with autopsy-confirmed pathology. These matched iPSC-derived patient-specific neurons and postmortem brain tissue will support studies of specific mechanisms that drive the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Cell stem cell 2017 JAN
Recent Zika Virus Isolates Induce Premature Differentiation of Neural Progenitors in Human Brain Organoids.
E. Gabriel et al.
Abstract
The recent Zika virus (ZIKV) epidemic is associated with microcephaly in newborns. Although the connection between ZIKV and neurodevelopmental defects is widely recognized, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here we show that two recently isolated strains of ZIKV, an American strain from an infected fetal brain (FB-GWUH-2016) and a closely-related Asian strain (H/PF/2013), productively infect human iPSC-derived brain organoids. Both of these strains readily target to and replicate in proliferating ventricular zone (VZ) apical progenitors. The main phenotypic effect was premature differentiation of neural progenitors associated with centrosome perturbation, even during early stages of infection, leading to progenitor depletion, disruption of the VZ, impaired neurogenesis, and cortical thinning. The infection pattern and cellular outcome differ from those seen with the extensively passaged ZIKV strain MR766. The structural changes we see after infection with these more recently isolated viral strains closely resemble those seen in ZIKV-associated microcephaly.
View All Publications


 网站首页
网站首页