概要
The simple protocol is performed in 2D adherent cultures. During the first 3 days, Medium A induces cells toward mesoderm. For the subsequent 4 days, mesodermal cells are further differentiated toward the hematopoietic lineage using Medium B. At Day 7, the medium is changed to Monocyte Differentiation Medium, which facilitates the differentiation to monocytes. CD14⁺ monocytes can be harvested directly from the culture supernatant starting as early as Day 14 and can be repeatedly harvested during the rest of the culture period. Peak CD14⁺ frequency is typically 60 - 80%.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 4 | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 5 | STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit | 05320 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
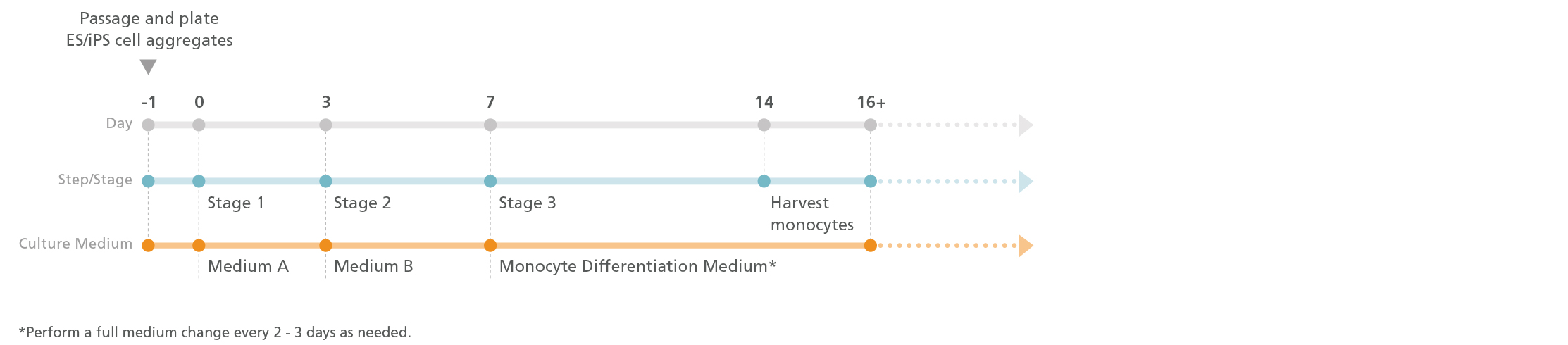
Figure 1. Monocyte Differentiation Protocol
One day prior to differentiation, human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) colonies are harvested and seeded as small aggregates (100 - 200 μm in diameter) at 10 - 20 aggregates/cm2 in mTeSR™1, TeSR™-E8™, or mTeSR™ Plus media. After one day, the medium is replaced with Medium A (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + Supplement A) to induce mesodermal specification (stage 1). On day 3, the medium is changed to Medium B (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + Supplement B) to promote hematopoietic specification (stage 2). On day 7, the medium is replaced with Monocyte Differentiation Medium (StemSpan™ SFEM II + STEMdiff™ Monocyte Differentiation Supplement) to promote the production of CD14+ monocytes (stage 3). Monocyte Differentiation Medium is used for all medium changes for the remaining culture period. CD14+ cells can be detected in suspension starting after day 14, and their frequency gradually increases until day 17 - 23. CD14+ cells can be harvested directly from the culture supernatant during medium changes.
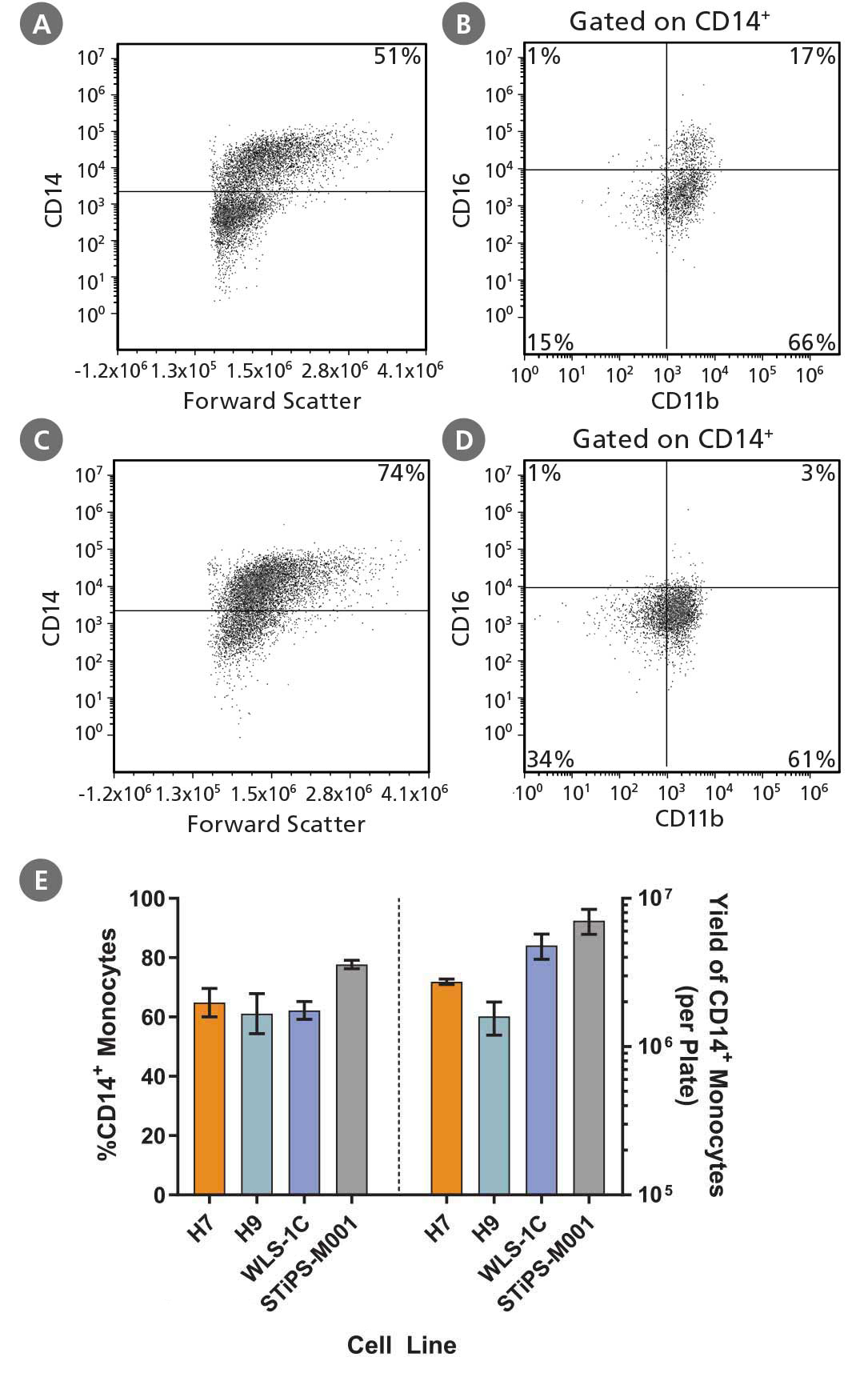
Figure 2. Robust and Efficient Generation of CD14⁺ Monocytes Using STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit
hPSCs were differentiated to monocytes using the 2D culture system described in Figure 1. Between days 17 and 23, cells were harvested every 2 - 3 days and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD14 expression. Representative flow cytometry plots are shown for (A, B) iPS (WLS-1C)-derived cells and (C, D) ES (H9)-derived cells. (E) The average frequency of viable CD14+ monocytes at the peak harvest was 61 - 78%. The average yield of CD14+ monocytes produced per 6-well plate at the peak harvest was between 1.6 x 10^6 and 7.1 x 10^6 cells. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 - 14).
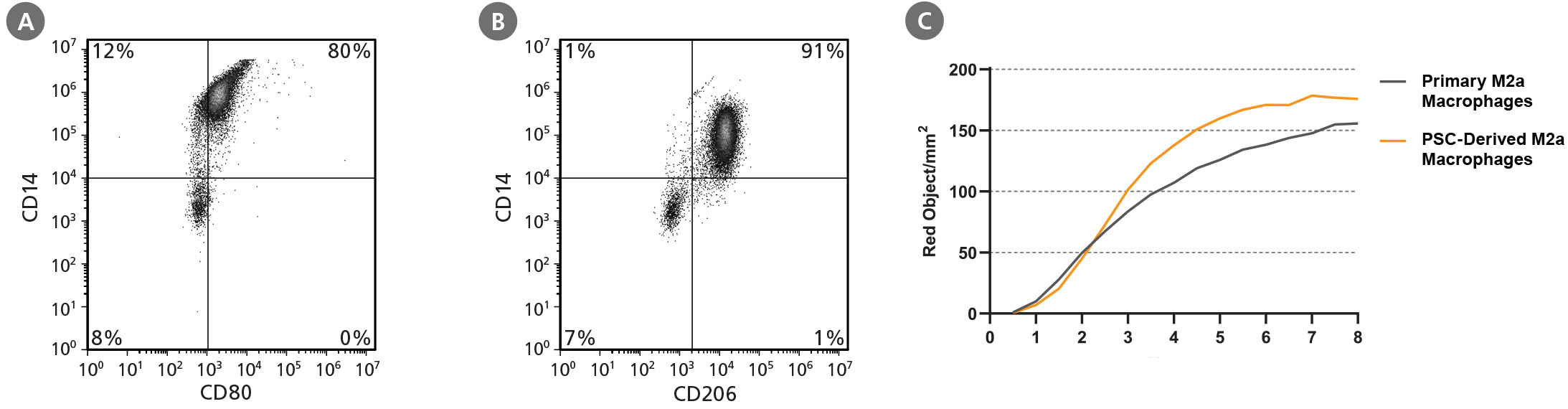
Figure 3. STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit Generates Monocytes That Are Capable of Differentiation to Macrophages
hPSC-derived monocytes were harvested after 21 days of culture. These were then differentiated to macrophages using ImmunoCult™-SF Macrophage Medium (Catalog #10961) with 100 ng/mL M-CSF for 4 days. Macrophages were then incubated for an additional 2 days with either 10 ng/mL of LPS and 50 ng/mL of IFN-γ, or 10 ng/mL IL-4, to become polarized to M1 or M2a macrophages, respectively. Representative flow cytometry plots of (A) M1 and (B) M2a macrophages produced from the WLS-1C iPS cell line are shown. (C) To measure phagocytosis, PSC-derived M2a macrophages and peripheral blood (PB) monocyte-derived M2a macrophages (primary M2a macrophages), were incubated with pHrodo™ Red Zymosan A BioParticles® Conjugate and incubated at 37°C for 8 hours. Images were acquired using the IncuCyte® ZOOM every 30 minutes and analyzed for internalization of pHrodo™ Red Zymosan A BioParticles® (measured as red object/mm2). hPSC-derived and primary M2a macrophages show similar phagocytic activity.
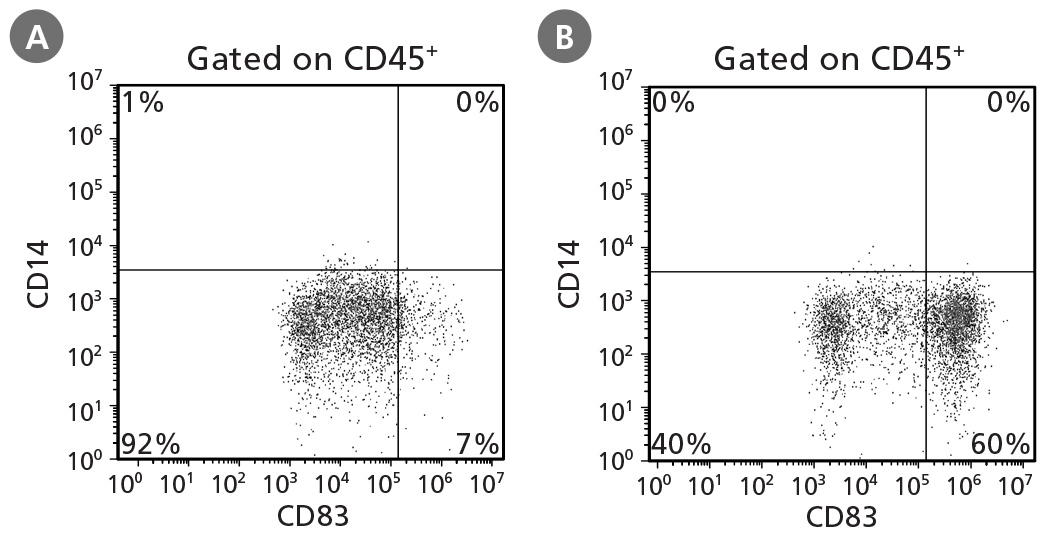
Figure 4. STEMdiff™ Monocyte Kit Generates Monocytes That Can Be Differentiated to Dendritic Cells
hPSCs were differentiated into monocytes, harvested after 21 days, and differentiated to dendritic cells using ImmunoCult™ Dendritic Cell Culture Kit (Catalog #10985). Half of the dendritic cells were harvested on day 7 and examined for CD14 and CD83 expression to identify CD14⁻CD83⁻/lo immature dendritic cells. The remaining dendritic cells were activated for 2 days and assessed for the presence of CD14⁻CD83⁺ mature dendritic cells at day 7. Representative cultures initiated with ES (H9) cells are shown for production of (A) immature dendritic cells and (B) mature dendritic cells.

 网站首页
网站首页