概要
STEMdiff™ MIM is a complete medium that produces a cell population enriched for early mesoderm, as indicated by positive expression of Brachyury (T) and NCAM markers. As part of the hPSC workflow, STEMdiff™ MIM efficiently differentiates hPSCs cultured in TeSR™ media. When directed, early mesoderm cells produced using STEMdiff™ MIM can be further differentiated to specialized cell types, such as osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes or endothelial cells. For more information, see the data below.
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet 1 | STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium | 05220, 05221 | 05220: Lot 18L97346B or lower; 05221: Lot 19B98885B or lower | English |
| Product Information Sheet 2 | STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium | 05220, 05221 | 05220: Lot 19E101752C or higher; 05221: Lot 19E101752B or higher | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium | 05220, 05221 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
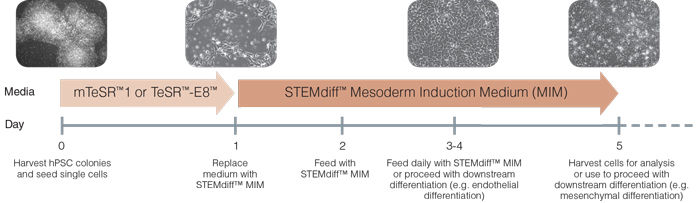
Figure 1. Schematic of Mesoderm Induction Medium Differentiation Timeline
On day 0, hPSC colonies are harvested and seeded as single cells at 5 x 10 4 /cm 2 in mTeSR™1 or TeSR™-E8™ and supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632. TeSR™ medium is replaced on day 1 with STEMdiff™ Mesoderm Induction Medium when cells are at approximately 20 - 50% confluency. Cells are then fed daily and cultured in STEMdiff™ MIM (days 2-4). Cells can be transferred to downstream differentiation conditions between days 3 - 5 or collected on day 5 for analysis.
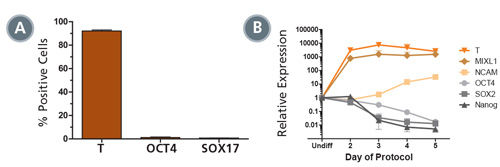
Figure 2. STEMdiff™ MIM Generates a Homogenous Population of T + OCT4 - Early Mesoderm
(A) Data showing marker expression characteristic of the early mesoderm (positive Brachyury (T) expression and negative OCT4 and SOX 17 expression) on day 5 of the protocol. Data is expressed as a mean percentage of cells expressing each marker ± SD, n = 33 (T, OCT4), n = 5 (SOX17). (B) Expression of undifferentiated cell markers (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG) and early mesoderm markers (T, MIXL1, NCAM), measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and normalized to levels in undifferentiated cells, n = 2.
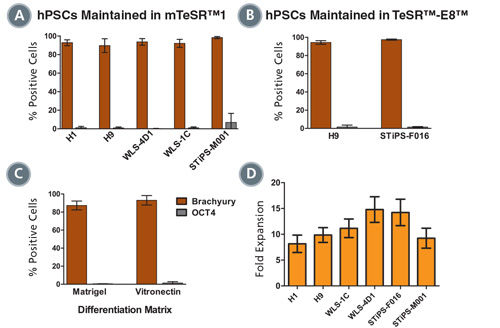
Figure 3. Mesoderm Differentiation and Cell Expansion are Efficient and Comparable Across Multiple hPSC Cell Lines
Graphs show mesoderm formation in multiple human ES (H1 and H9) and iPS (WLS-4D1, WLS-1C, STiPS-M001 and STiPS-F016) cell lines as measured by expression of Brachyury (T) and absence of OCT4. Cells maintained in (A) mTeSR™1 or (B) TeSR™-E8™ medium were differentiated using STEMdiff™MIM. (A, n = 2 - 10 per cell line, B, n = 3, data are expressed as a mean percentage ± SD) (C) Mesoderm differentiation on Corning® Matrigel® or Vitronectin XF™ is comparable. (n = 5, data are the mean percentage ± SD) (D) Average fold expansion of cells cultured in STEMdiff™MIM, as determined by cell yield / cells seeded. (n = 3 - 13. Error bars indicate SEM)
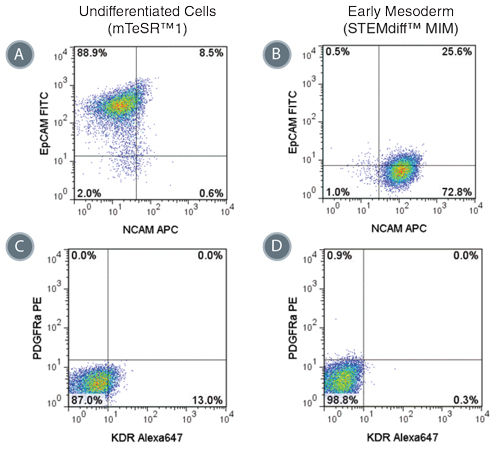
Figure 4. Phenotype of Cells Treated with STEMdiff™ MIM is Consistent with Early Mesoderm
Representative flow cytometry plots showing the switch from (A) EpCAM + NCAM -/low in hPSCs cultured in mTeSR™1 to (B) EpCAM -/low NCAM + expression in STEMdiff™ MIM-treated cells (day 5). EpCAM -/low NCAM + expression is characteristic of the early mesoderm. Expression of PDGFRα and KDR are low in both (C) hPSCs cultured in mTeSR™1 and (D) early mesoderm cells derived with STEMdiff™ MIM.
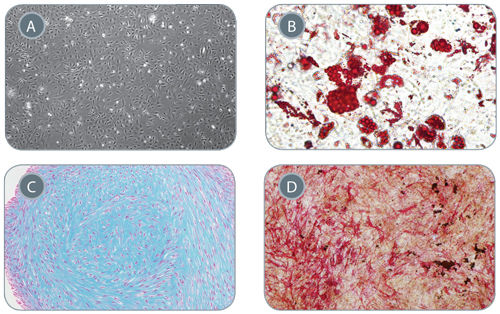
Figure 5. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Early Mesoderm Cells Can Be Further Differentiated in In Vitro Assays
(A) Early mesoderm cells generated with the 5-day STEMdiff™ MIM protocol and subsequently cultured with MesenCult™-ACF develop mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like morphology, 40X magnifi cation. MSC-like cells can subsequently differentiate into (B) adipocytes (Oil Red O staining), 200x magnification, (C) chondrocytes (Alcian Blue staining), 100X magnification, and (D) osteogenic cells (Fast Red and Silver Nitrate staining), 40X magnification.
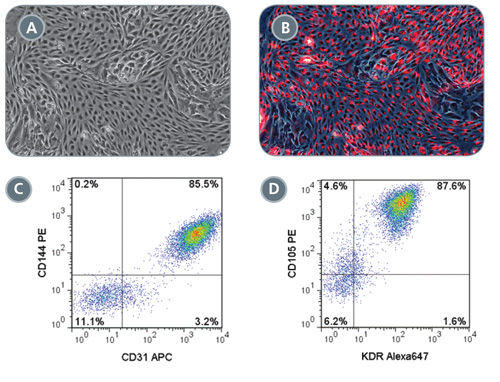
Figure 6. Robust Endothelial Differentiation of STEMdiff™ MIM-Generated Early Mesoderm Cells
On day 3 of the STEMdiff™ MIM protocol, early mesoderm cells were switched to a downstream endothelial differentiation protocol based on Tan et al. (A) Differentiated cells display characteristic endothelial cell morphology and (B) are able to uptake Dil-Ac-LDL (red). Representative flow cytometry plots showing (C) 85.5% CD144 + CD31 + and (D) 87.6% CD105 + KDR + expression in differentiated endothelial cells.

 网站首页
网站首页