概要
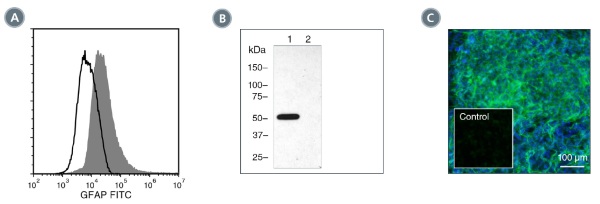
The 2E1.E9 antibody reacts with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), an ~49 kDa type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that, within the central nervous system, is expressed primarily by astrocytes, though found at high levels in some glial-derived tumors. GFAP is thought to contribute to the structural architecture and strength of the cytoskeleton. The 2E1.E9 antibody does not cross-react with other IF proteins and can be used to distinguish astrocytes from other glial cells. GFAP has also been identified in Leydig cells, keratinocytes, chondrocytes and osteocytes. The GFAP polypeptide comprises an N-terminal head, a central rod, and a C-terminal tail domain, and assembles as dimers by a process dependent on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the N-terminal domain. Several splice variants have been identified, encoding three distinct isoforms. Many mutations in the GFAP gene (>50) have been associated with Alexander disease, a progressive leukoencephalopathy characterized by cytoplasmic inclusions and dysfunctional myelination.
This antibody clone has been verified for labeling neural stem and progenitor cells grown in NeuroCult™ NS-A Proliferation Kit (Human; Catalog #05751) and NeuroCult™ Proliferation Kit (Mouse; Catalog #05702).
数据及文献
Publications (1)
Gene 2014 JAN
Onset of rosette formation during spontaneous neural differentiation of hESC and hiPSC colonies
Malchenko S et al.
Abstract
In vitro neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) is an advantageous system for studying early neural development. The process of early neural differentiation in hESCs begins by initiation of primitive neuroectoderm, which is manifested by rosette formation, with consecutive differentiation into neural progenitors and early glial-like cells. In this study, we examined the involvement of early neural markers - OTX2, PAX6, Sox1, Nestin, NR2F1, NR2F2, and IRX2 - in the onset of rosette formation, during spontaneous neural differentiation of hESC and human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) colonies. This is in contrast to the conventional way of studying rosette formation, which involves induction of neuronal differentiation and the utilization of embryoid bodies. Here we show that OTX2 is highly expressed at the onset of rosette formation, when rosettes comprise no more than 3-5 cells, and that its expression precedes that of established markers of early neuronal differentiation. Importantly, the rise of OTX2 expression in these cells coincides with the down-regulation of the pluripotency marker OCT4. Lastly, we show that cells derived from rosettes that emerge during spontaneous differentiation of hESCs or hiPSCs are capable of differentiating into dopaminergic neurons in vitro, and into mature-appearing pyramidal and serotonergic neurons weeks after being injected into the motor cortex of NOD-SCID mice. ?? 2013 Elsevier B.V.
View All Publications

 网站首页
网站首页